Which two statements are true for GRE tunneling? (Choose two.)
GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) tunnels allow for encapsulation of a wide variety of network layer protocols inside virtual point-to-point links. For a GRE tunnel to function, the endpoints must have a valid route to the remote endpoint to ensure that traffic can be properly routed to the tunnel's destination. Additionally, GRE tunnels support multiple logical units per interface, allowing for different logical connections to be configured on the same physical interface.
Click the Exhibit button.
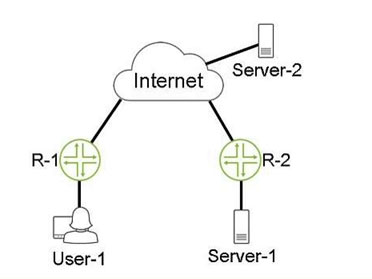
Referring to the exhibit, the GRE tunnel between R-1 and R-2 allows connectivity between User-1 and Server-1. When User-1 communicates with Server-2 with packets that are 1472 bytes in size, no packet fragmentation occurs. User-1 can communicate with Server-1 with packets that are up to 1448 bytes in size with no packet fragmentation. However, if the packet size is larger than 1448 bytes, packet fragmentation occurs.
Why is the packet fragmentation occurring between User-1 and Server-1 in this scenario?
Packet fragmentation occurs between User-1 and Server-1 because of the additional overhead added by the GRE tunnel. GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) encapsulates packets, adding 24 bytes of additional header information to each packet. Normally, an Ethernet frame can handle a payload of up to 1500 bytes. When the packet size from User-1 to Server-2 is 1472 bytes, the network can accommodate it without fragmentation. However, when communicating through the GRE tunnel, the extra 24-byte GRE header means the largest packet that can be transmitted without fragmentation is 1476 bytes (1500 - 24). Thus, for communication between User-1 and Server-1, packets larger than 1448 bytes (1500 - 24 - 28 for IP header) will get fragmented.
What happens when a packet matches a static route with the next hop parameter set to reject?
When a packet matches a static route with the next hop parameter set to reject, the packet is dropped, and an ICMP message is sent to the source indicating that the destination is unreachable. This behavior helps notify the sender of the issue rather than silently dropping the packet, which would leave the sender unaware of the problem.
Which two statements are correct about the BGP MED attribute? (Choose two.)
The BGP MED attribute is used to influence the path selection process when multiple paths exist to the same destination from different autonomous systems (AS). Specifically, BGP uses the MED value when peering to two or more connections to the same upstream AS, helping to determine the preferred path. Additionally, if the MED attribute is not explicitly defined, BGP assumes the MED value to be 0.
What is the Junos default router priority advertisement value for IS-IS?
The default router priority advertisement value for IS-IS in Junos is 64. This is the value that is assigned by default to routers for priority in IS-IS protocol. The priority value determines the designated intermediate system (DIS) on a LAN segment, and Junos sets this to 64 unless it is explicitly configured otherwise.