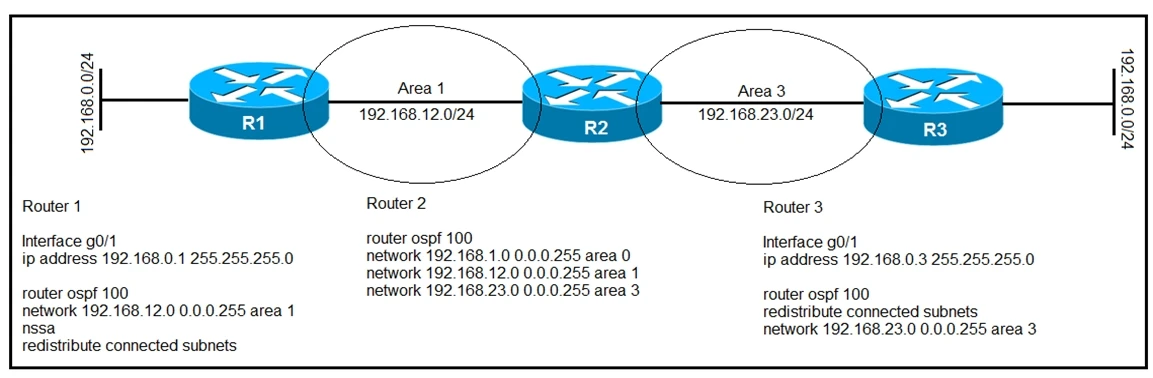
Refer to the exhibit. After troubleshooting an OSPF adjacency issue, routers 1, 2, and 3 have formed OSPF neighbor relationships. Which statement about the configuration is true?

Router 2 will use Router 1 as the next hop for the network 192.168.0.0/24. According to the OSPF path selection, the preference order is O > O IA > N1 > E1 > N2 > E2. In this scenario, Router 2 is connected to Area 0, Area 1, and Area 3, and it will prefer routes learned from OSPF NSSA Type 7 (N2) LSAs over Type 5 (E2) LSAs if both are available. Since Router 1 is injecting the 192.168.0.0/24 network as a Type 7 LSA in the NSSA Area 1, Router 2 will prefer this optimal path over any Type 5 LSA route.