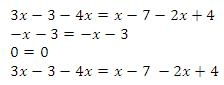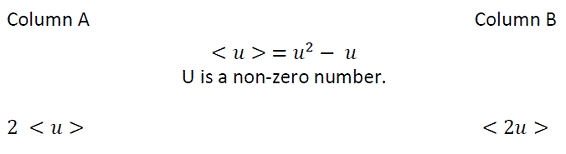
Question 6 of 49
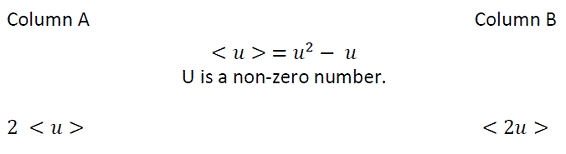
Correct Answer: A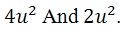
A
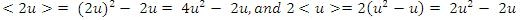
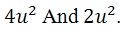
You can cancel out the term -2u from both columns, which leaves a comparison between
As you can see, Quantity A> Quantity B.
Question 7 of 49

The toll for driving on road A is $1.20 for the first mile and 35 cents for each additional mile. The toll for driving on road B is $2.25 for the first mile and 20 cents for each additional mile.

Correct Answer: C
To calculate the toll for an 8-mile drive on both roads, we break down the costs as follows. For road A, the cost for the first mile is $1.20 and 35 cents for each additional mile. The additional miles are 7, so the total cost is $1.20 + (7 * $0.35) = $1.20 + $2.45 = $3.65. For road B, the cost for the first mile is $2.25 and 20 cents for each additional mile. Again, the additional miles are 7, so the total cost is $2.25 + (7 * $0.20) = $2.25 + $1.40 = $3.65. Both tolls are equal.
Question 8 of 49

Ps age is twice Qs age. One year ago, Rs age was exactly half of Ps age at that time.

Correct Answer: A
Let P's age be 2Q since P's age is twice Q's age. One year ago, P's age would have been 2Q - 1 and R's age would have been (2Q - 1) / 2. This means R's current age is greater than (2Q - 1) / 2 + 1 = (2Q + 1) / 2, which will always be greater than Q's current age as long as Q's age is positive. Thus, the quantity in Column A is greater.
Question 9 of 49
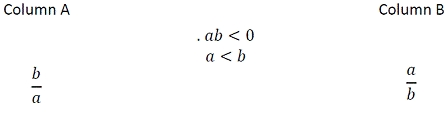
Correct Answer:
Explanation
The inequality ab< 0 tells you that either a or b, but not both, is negative. Since a On the other hand, if a= -2 and b= 1, then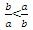 comparison between Quantity A and Quantity B. Which is greater depends on the absolute values of the two variables. For example, if a= -1 and b= 2, then
comparison between Quantity A and Quantity B. Which is greater depends on the absolute values of the two variables. For example, if a= -1 and b= 2, then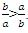
Question 10 of 49
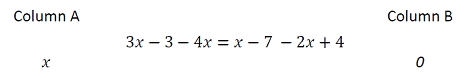
Correct Answer: C
D
All terms on both sides cancel out: