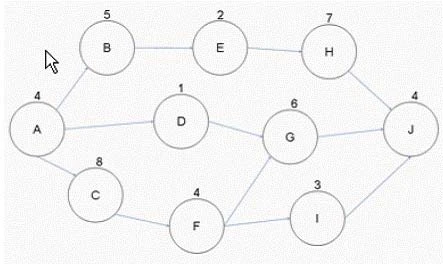
If Activity B takes eight days to complete instead of five days as schedule, how long can you now delay Activity H?

Activity H must be analyzed within the context of the critical path of the project. Initially, the path under consideration (A-B-E-H-J) has a duration of 26 days, assuming B takes 5 days. If Activity B is extended to 8 days, it consumes 3 additional days out of its float time. Thus, the float usage does not directly impact the critical path duration immediately as other paths might still remain longer. However, considering the critical path dynamics and without extensive float recalculations, if Activity H delays any further, it might push the entire project timeline over its limit, leading to zero days of allowable delay for Activity H.
A milestone is a significant point or event in the project. It marks important stages in the project lifecycle, signifying the completion of major phases or key deliverables. Milestones serve as checkpoints to assess the project's progress, but they do not necessarily have to be linked to specific dates. They help in evaluating performance and guiding the direction of the project.
Identification of project risks is not part of the process improvement plan. Identifying risks falls under risk management and is documented in the risk register. The process improvement plan focuses on refining existing processes, which includes defining process boundaries, configuring processes, and setting targets for improved performance.
Schedule variance (SV) is calculated using the formula SV = EV - PV, where EV is the Earned Value and PV is the Planned Value. Given that the project budget is $778,000 and the project should be 50% complete at the end of the second quarter, the Planned Value (PV) is 50% of $778,000, which is $389,000. The Earned Value (EV) is 40% of $778,000, which is $311,200. The schedule variance (SV) would therefore be $311,200 - $389,000, which equals -$77,800, indicating the project is behind schedule.
Conformance to the project schedule at 0.95 means that the project's schedule can deviate no more than five percent from the planned schedule. This is a measure of how strictly the project must adhere to its planned schedule, ensuring that variance in timing is kept within this narrow range.