Which dataplane layer of the graphic shown provides pattern protection for spyware and vulnerability exploits on a Palo Alto Networks Firewall?
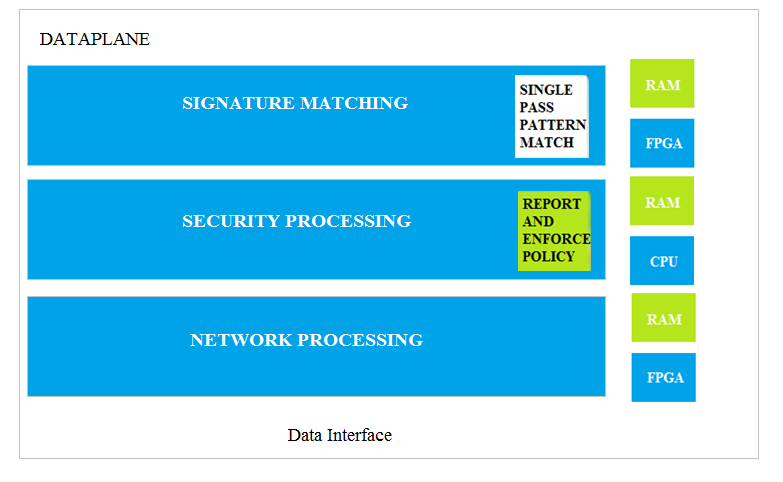
Which dataplane layer of the graphic shown provides pattern protection for spyware and vulnerability exploits on a Palo Alto Networks Firewall?

The Signature Matching layer provides pattern protection for spyware and vulnerability exploits. This layer uses single pass pattern matching to identify and block known threats effectively. Security processing focuses on policy enforcement and reporting rather than directly matching threat patterns, while network processing handles basic network operations.
Which option shows the attributes that are selectable when setting up application filters?
The correct attributes selectable when setting up application filters are Category, Subcategory, Risk, Standard Ports, and Technology. These are the relevant attributes typically considered for configuring application filters as they provide a comprehensive overview that includes not just the categories and risks but also the standard ports and technology used by the applications.
Actions can be set for which two items in a URL filtering security profile? (Choose two.)
In a URL filtering security profile, actions such as block, alert, continue, override, or allow can be set for specific categories of URLs. These categories are either custom URL categories, which administrators define to control access to particular URLs relevant to their organization's security policy, or PAN-DB URL categories, which are predefined URL categories provided by the PAN-DB database. Both types allow administrators to specify the desired actions based on organizational needs.
DRAG DROP -
Match the Cyber-Attack Lifecycle stage to its correct description.
Select and Place:


Which two statements are correct about App-ID content updates? (Choose two.)
Updated application content might change how Security policy rules are enforced. This is because new App-IDs and modifications to existing App-IDs can cause the firewall to categorize and handle applications differently. Additionally, after an application content update, new applications are automatically identified and classified by the firewall. This automatic identification and classification reduces manual administrative effort and ensures that the security policies are up to date with the latest application signatures.