Mysq1> ALTER TABLE employees ADD FOREIGN KEY (Department_ID) REFERENCES departments (Department_ID);
ERROR 1215 (HY000): cannot add foreign key constraint
Which command will provide additional information about the error?
To configure a PHP application to use the UTF8 character set, you can use the 'mysqli::set_charset' method to set the character set for a MySQLi connection and configure the PDO object to set the character set in the DSN string. Therefore, the correct methods are using 'mysqli::set_charset('utf8')' and setting the charset in the PDO DSN string like 'new PDO('mysql:host=localhost;dbname=test;charset=utf8', 'user', 'pass');'.
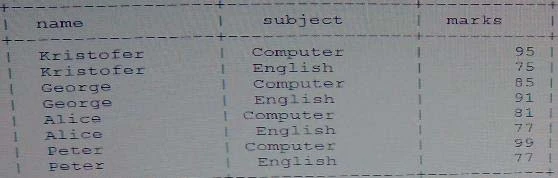
Assuming You want to see this output:

Which query achieves the preceding result?
In MySQL, valid identifiers for database and table names can be enclosed in backticks, single quotes, or used without any quotes provided they adhere to naming rules. Option B uses single quotes around the full identifier 'mysq1. user', which is valid. Option C properly encloses both the database name and table name in single quotes, ensuring the identifier is interpreted correctly. Option D shows a version with a combination of a regular database name and a quoted table name, which is also allowed in some MySQL contexts. Option A contains a typo, which makes it invalid. Option E has improper quotation marks around the identifier, which disqualifies it as a valid identifier.