The following is a sample of the data.

You need to select a partition key that meets the following requirements for writes:
✑ Minimizes the partition skew
✑ Avoids capacity limits
✑ Avoids hot partitions
What should you do?

Using a synthetic key that combines deviceId with a random number is beneficial for this scenario as it helps to distribute write operations evenly across multiple partitions. This approach minimizes the chances of hitting capacity limits and avoids creating hot partitions, where one partition might receive significantly more writes than others. Options involving timestamp, sensor1Value, or deviceManufacturer could still lead to uneven data distribution, causing hot partitions or partition skew.
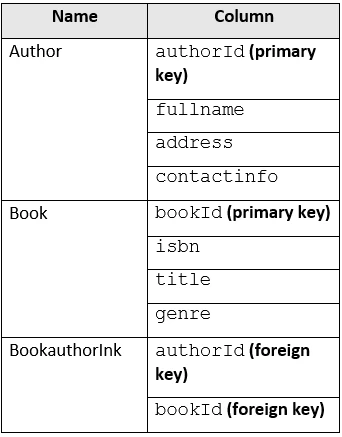
The most optimal approach to minimize latency and read operation costs in this scenario is to create a container that contains a document for each Author and a document for each Book, and then embed the authorId in each Book document. This design takes advantage of Cosmos DB's ability to store related entities within the same container and makes querying more efficient, especially for the most common query, which lists books by a given authorId. Embedding authorId in each Book document keeps the data structure simple and avoids the complexities and potential overhead associated with multiple containers or cross-container joins.

The IS_NUMBER function in Azure Cosmos DB returns a Boolean value indicating whether the specified expression is a number. For the given query: IS_NUMBER('1234') evaluates to false because '1234' is a string, not a number. IS_NUMBER(1234) evaluates to true because 1234 is a number. IS_NUMBER({prop: 1234}) evaluates to false because the argument provided is an object, not a number. Therefore, the output of the query is [ {"A": false, "B": true, "C": false} ].
To ensure that a trigger runs before an item is inserted into a container in Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API, you need to register the trigger as a pre-trigger and set the trigger name in RequestOptions for each create request. Registering the trigger as a pre-trigger ensures it is configured to run before the insertion operation. Setting the trigger name in RequestOptions ensures that the trigger is actually executed during the specific operation.