Which of the following commands can be used to resolve a DNS name to an IP address?
The correct command to resolve a DNS name to an IP address is 'host'. This command queries DNS servers to obtain the respective IP address of a given hostname.
Which of the following outputs comes from the command free?
A.

B.
C.

D.

E.
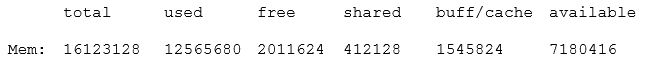
The 'free' command is used to display the amount of free and used memory in the system. It provides a detailed report on the system's memory usage including the total, used, and free memory. Based on the provided outputs, option E shows a detailed memory usage summary indicating total, used, free, shared, buffer/cache, and available memory. Hence, the correct answer is E.
What is true about the dmesg command? (Choose two.)
The dmesg command displays the content of the Linux kernel's ring buffer, which contains system messages and diagnostic information. Additionally, the ring buffer has a limited size, and when it becomes full, the oldest messages are overwritten by newer information. Therefore, dmesg might not display older information if it has been replaced by newer entries.
Which of the following outputs could stem from the command last?
The command 'last' in Unix/Linux environments shows a listing of last logged in users. The format of the output includes the username, terminal, login and logout dates and times, and the duration of the login session. Option E shows this format with the user 'root', terminal 'tty2', and login and logout times on 'Wed May 17'. Therefore, option E is the correct answer.
What is the UID of the user root?
In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, the user identifier (UID) for the root user is 0. This is a standard convention where the root user, also known as the superuser, has the highest level of system privileges and is denoted by the UID 0.