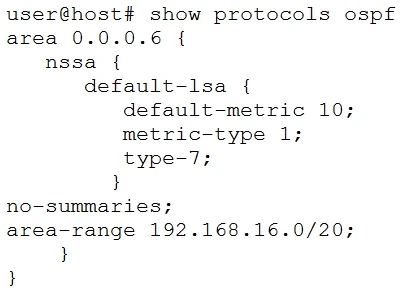
Referring to the ABR configuration shown in the exhibit, which three statements are correct? (Choose three.)

The ABR advertises a default route to the NSSA using a Type 7 LSA. The 'no-summaries' keyword prevents the ABR from summarizing internal Type 1 and Type 2 LSAs, which implies that OSPF will not create any summary routes within the 192.168.16.0/20 range. The ABR converts the Type 7 LSAs from the NSSA into Type 5 LSAs before they are sent to the backbone area, but this is done for each Type 7 LSA individually rather than as a single aggregated Type 5 LSA. Therefore, the ABR does not summarize any routes within the 192.168.16.0/20 range.
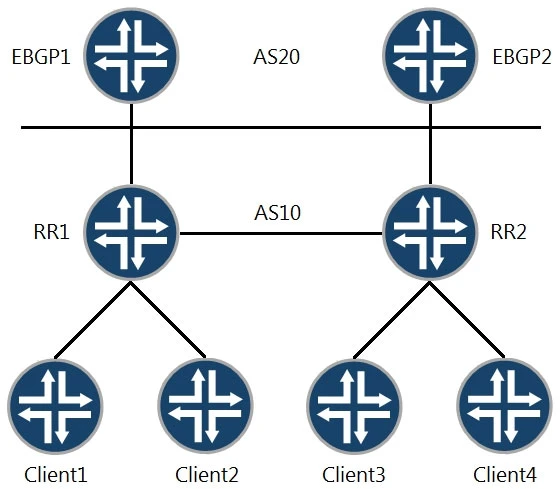
In a route reflector setup like the one shown in the exhibit, the following statements are correct: RR2 advertises routes learned from Client3 to EBGP2 with itself as the next hop. This is typical in BGP configurations where the route reflector (RR2 in this case) ensures that external BGP peers (EBGP2) receive the routes with the next hop set to the RR. Additionally, RR2 adds its cluster ID when advertising routes from Client4 to Client3. This is a common practice to prevent routing loops, as the cluster ID acts as an identifier for the route reflector cluster.
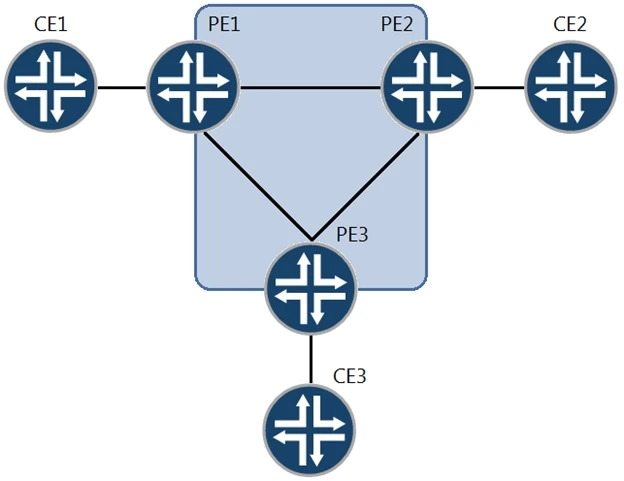
In the given network diagram involving Layer 2 circuits between CE1, CE2, and CE3, Layer 2 circuits are typically point-to-point links. For each Layer 2 circuit, a separate VLAN is needed to uniquely identify the traffic on that circuit. Therefore, two VLANs must be configured from PE1 to CE1 to establish the necessary point-to-point connections. This ensures that each Layer 2 circuit is isolated and correctly set up to connect the different customer edge devices through the provider edge devices.
For a BGP Layer 2 VPN, the VRF table typically stores the following information: the Layer 2 encapsulation, the local site ID, and the logical interfaces provisioned to the local CE device. Layer 2 encapsulation is necessary to define how data frames are encapsulated over the VPN. The local site ID uniquely identifies the local site within the VPN. Finally, logical interfaces provisioned to the local CE device are necessary for routing and switching the traffic within the VPN.
Wide metrics are sent by default in IS-IS and use 24 bits in TLVs to send information. Disabling narrow metrics can result in external routes being leaked from L1 to L2 areas automatically. This behavior occurs because only wide metrics are used when narrow metrics are disabled, facilitating route leaking without the need for an export policy.