Community votes
No votes yet
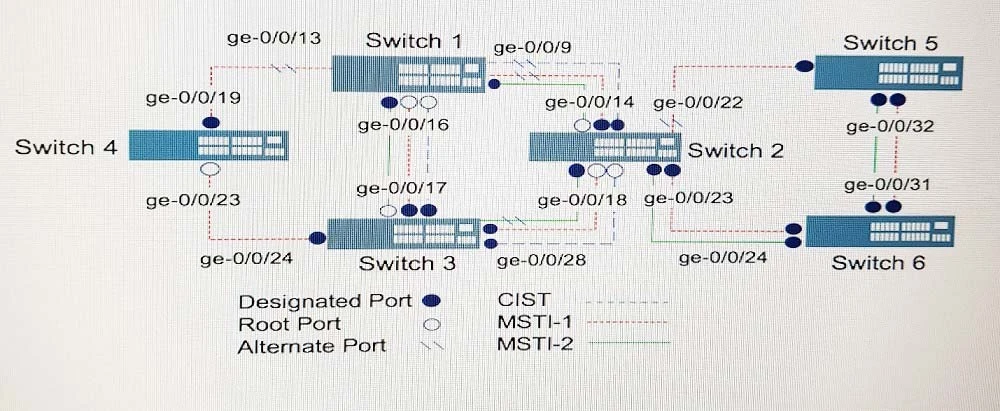
Referring to the exhibit, what is the minimum number of MSTP regions where the topology would be implemented?
The minimum number of MSTP regions required for the topology to be implemented is one. In Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP), a single region can contain multiple MST instances (MSTIs). Each MSTI can have its own spanning tree, allowing separate topologies within the same MSTP region. Therefore, only one MSTP region is necessary to manage the different instances depicted in the topology.
Community votes
No votes yet

You are asked to advertise the 1.0.0.0/8 and 1.5.5.5/32 routes to your 10.254.32.2 BGP peer.
Referring to the exhibit, which configuration change would satisfy this requirement?
To advertise the 1.0.0.0/8 and 1.5.5.5/32 routes to the BGP peer at 10.254.32.2, the configuration change needed involves making sure that the export policy matches the routes correctly. Since term 1 in the export-to-as81 policy uses the filter '1.0.0.0/8 longer' to match prefixes that are more specific than 1.0.0.0/8, changing it to '1.0.0.0/8 or longer' will include the exact match 1.0.0.0/8 as well as any more specific prefixes, including 1.5.5.5/32. This will ensure both required routes are advertised.
Community votes
No votes yet
Which action will accomplish?
To address the issue of massive dropped packets due to highly oversubscribed bandwidth on the campus EX9200 core devices, you need to implement output traffic shaping directly on the interfaces. The correct configuration requires applying the shaping rate parameter under the appropriate class-of-service hierarchy. Specifically, applying the shape-rate 5G parameter to all interfaces under the [edit class-of-service] hierarchy ensures that traffic shaping is correctly configured at the interface level, effectively managing the bandwidth.
Community votes
No votes yet
Community votes
No votes yet