Given:
 and the code fragment:
and the code fragment:
What is the result?
Given:
 and the code fragment:
and the code fragment:
What is the result?
B
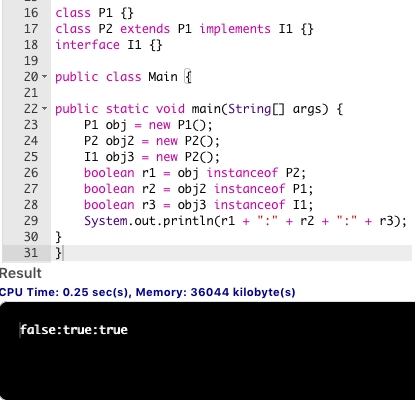
The answer is B because P2 has inherited from P1 therefore any object of P2 can be called P1's instance.
Answer is B. class P1{} class P2 extends P1 implements I1 {} interface I1{} public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { P1 obj = new P1(); P2 obj2 = new P2(); I1 obj3 = new P2(); boolean r1 = obj instanceof P2; boolean r2 = obj2 instanceof P1; boolean r3 = obj3 instanceof I1; System.out.println(r1 + ":" + r2 + ":" + r3); } }