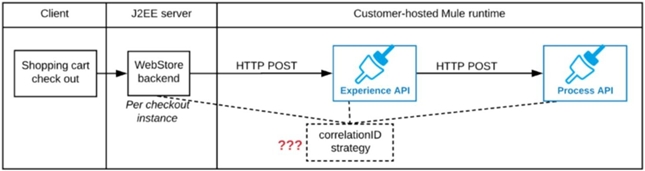
Refer to the exhibit. A shopping cart checkout process consists of a web store backend sending a sequence of API invocations to an Experience API, which in turn invokes a Process API. All API invocations are over HTTPS POST. The Java web store backend executes in a Java EE application server, while all API implementations are Mule applications executing in a customer-hosted Mule runtime.
End-to-end correlation of all HTTP requests and responses belonging to each individual checkout instance is required. This is to be done through a common correlation ID, so that all log entries written by the web store backend, Experience API implementation, and Process API implementation include the same correlation ID for all requests and responses belonging to the same checkout instance.
What is the most efficient way (using the least amount of custom coding or configuration) for the web store backend and the implementations of the Experience
API and Process API to participate in end-to-end correlation of the API invocations for each checkout instance?