HOTSPOT -
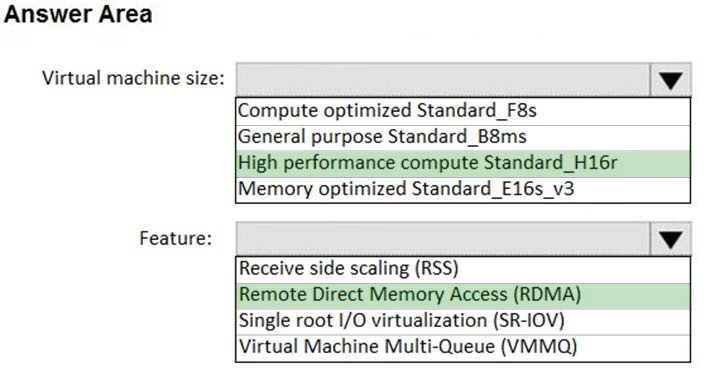
You plan to deploy a network-intensive application to several Azure virtual machines.
You need to recommend a solution that meets the following requirements:
✑ Minimizes the use of the virtual machine processors to transfer data
✑ Minimizes network latency
Which virtual machine size and feature should you use? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area: