HOTSPOT -
Case study -
This is a case study. Case studies are not timed separately. You can use as much exam time as you would like to complete each case. However, there may be additional case studies and sections on this exam. You must manage your time to ensure that you are able to complete all questions included on this exam in the time provided.
To answer the questions included in a case study, you will need to reference information that is provided in the case study. Case studies might contain exhibits and other resources that provide more information about the scenario that is described in the case study. Each question is independent of the other questions in this case study.
At the end of this case study, a review screen will appear. This screen allows you to review your answers and to make changes before you move to the next section of the exam. After you begin a new section, you cannot return to this section.
To start the case study -
To display the first question in this case study, click the Next button. Use the buttons in the left pane to explore the content of the case study before you answer the questions. Clicking these buttons displays information such as business requirements, existing environment, and problem statements. If the case study has an All Information tab, note that the information displayed is identical to the information displayed on the subsequent tabs. When you are ready to answer a question, click the Question button to return to the question.
Overview -
Litware, Inc. is a manufacturing company that has offices throughout North America. The analytics team at Litware contains data engineers, analytics engineers, data analysts, and data scientists.
Existing Environment -
Fabric Environment -
Litware has been using a Microsoft Power BI tenant for three years. Litware has NOT enabled any Fabric capacities and features.
Available Data -
Litware has data that must be analyzed as shown in the following table.

The Product data contains a single table and the following columns.

The customer satisfaction data contains the following tables:
Survey -
Question -
Response -
For each survey submitted, the following occurs:
One row is added to the Survey table.
One row is added to the Response table for each question in the survey.
The Question table contains the text of each survey question. The third question in each survey response is an overall satisfaction score. Customers can submit a survey after each purchase.
User Problems -
The analytics team has large volumes of data, some of which is semi-structured. The team wants to use Fabric to create a new data store.
Product data is often classified into three pricing groups: high, medium, and low. This logic is implemented in several databases and semantic models, but the logic does NOT always match across implementations.
Requirements -
Planned Changes -
Litware plans to enable Fabric features in the existing tenant. The analytics team will create a new data store as a proof of concept (PoC). The remaining Liware users will only get access to the Fabric features once the PoC is complete. The PoC will be completed by using a Fabric trial capacity
The following three workspaces will be created:
AnalyticsPOC: Will contain the data store, semantic models, reports pipelines, dataflow, and notebooks used to populate the data store
DataEngPOC: Will contain all the pipelines, dataflows, and notebooks used to populate OneLake
DataSciPOC: Will contain all the notebooks and reports created by the data scientists
The following will be created in the AnalyticsPOC workspace:
A data store (type to be decided)
A custom semantic model -
A default semantic model -
Interactive reports -
The data engineers will create data pipelines to load data to OneLake either hourly or daily depending on the data source. The analytics engineers will create processes to ingest, transform, and load the data to the data store in the AnalyticsPOC workspace daily. Whenever possible, the data engineers will use low-code tools for data ingestion. The choice of which data cleansing and transformation tools to use will be at the data engineers’ discretion.
All the semantic models and reports in the Analytics POC workspace will use the data store as the sole data source.
Technical Requirements -
The data store must support the following:
Read access by using T-SQL or Python
Semi-structured and unstructured data
Row-level security (RLS) for users executing T-SQL queries
Files loaded by the data engineers to OneLake will be stored in the Parquet format and will meet Delta Lake specifications.
Data will be loaded without transformation in one area of the AnalyticsPOC data store. The data will then be cleansed, merged, and transformed into a dimensional model
The data load process must ensure that the raw and cleansed data is updated completely before populating the dimensional model
The dimensional model must contain a date dimension. There is no existing data source for the date dimension. The Litware fiscal year matches the calendar year. The date dimension must always contain dates from 2010 through the end of the current year.
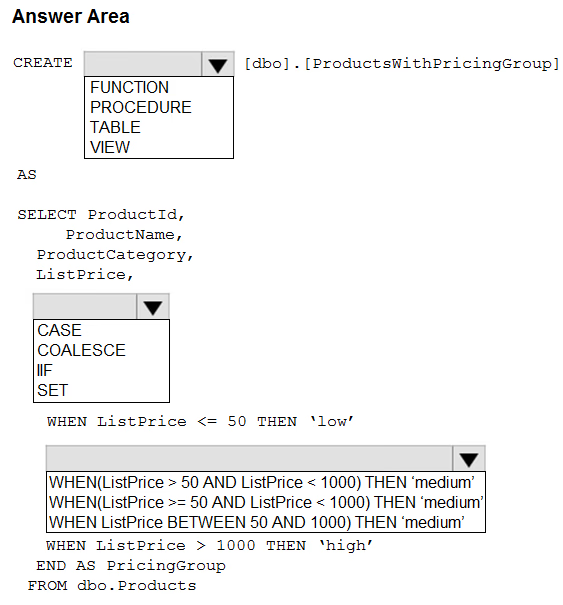
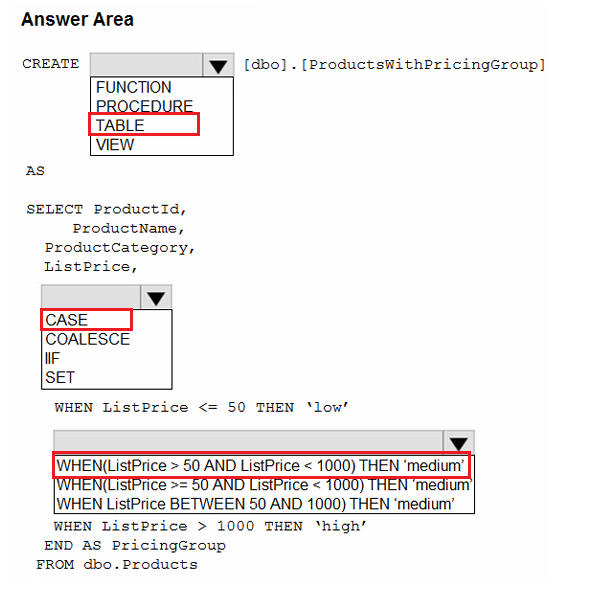
The product pricing group logic must be maintained by the analytics engineers in a single location. The pricing group data must be made available in the data store for T-SOL. queries and in the default semantic model. The following logic must be used:
List prices that are less than or equal to 50 are in the low pricing group.
List prices that are greater than 50 and less than or equal to 1,000 are in the medium pricing group.
List prices that are greater than 1,000 are in the high pricing group.
Security Requirements -
Only Fabric administrators and the analytics team must be able to see the Fabric items created as part of the PoC.
Litware identifies the following security requirements for the Fabric items in the AnalyticsPOC workspace:
Fabric administrators will be the workspace administrators.
The data engineers must be able to read from and write to the data store. No access must be granted to datasets or reports.
The analytics engineers must be able to read from, write to, and create schemas in the data store. They also must be able to create and share semantic models with the data analysts and view and modify all reports in the workspace.
The data scientists must be able to read from the data store, but not write to it. They will access the data by using a Spark notebook
The data analysts must have read access to only the dimensional model objects in the data store. They also must have access to create Power BI reports by using the semantic models created by the analytics engineers.
The date dimension must be available to all users of the data store.
The principle of least privilege must be followed.
Both the default and custom semantic models must include only tables or views from the dimensional model in the data store. Litware already has the following Microsoft Entra security groups:
FabricAdmins: Fabric administrators
AnalyticsTeam: All the members of the analytics team
DataAnalysts: The data analysts on the analytics team
DataScientists: The data scientists on the analytics team
DataEngineers: The data engineers on the analytics team
AnalyticsEngineers: The analytics engineers on the analytics team
Report Requirements -
The data analysts must create a customer satisfaction report that meets the following requirements:
Enables a user to select a product to filter customer survey responses to only those who have purchased that product.
Displays the average overall satisfaction score of all the surveys submitted during the last 12 months up to a selected dat.
Shows data as soon as the data is updated in the data store.
Ensures that the report and the semantic model only contain data from the current and previous year.
Ensures that the report respects any table-level security specified in the source data store.
Minimizes the execution time of report queries.
You need to resolve the issue with the pricing group classification.
How should you complete the T-SQL statement? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.