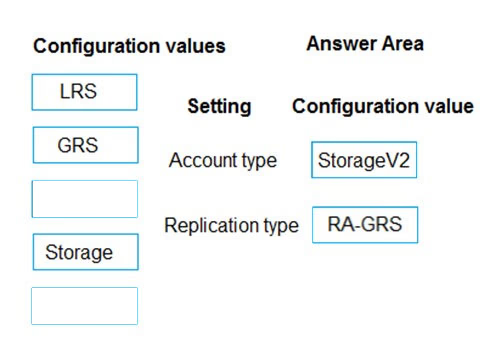
Account type: StorageV2 -
You must create new storage accounts as type StorageV2 (general-purpose V2) to take advantage of Data Lake Storage Gen2 features.
Scenario: Polling data is stored in one of the two locations:
✑ An on-premises Microsoft SQL Server 2019 database named PollingData
✑ Azure Data Lake Gen 2
Data in Data Lake is queried by using PolyBase
Replication type: RA-GRS -
Scenario: All services and processes must be resilient to a regional Azure outage.
Geo-redundant storage (GRS) is designed to provide at least 99.99999999999999% (16 9's) durability of objects over a given year by replicating your data to a secondary region that is hundreds of miles away from the primary region. If your storage account has GRS enabled, then your data is durable even in the case of a complete regional outage or a disaster in which the primary region isn't recoverable.
If you opt for GRS, you have two related options to choose from:
✑ GRS replicates your data to another data center in a secondary region, but that data is available to be read only if Microsoft initiates a failover from the primary to secondary region.
✑ Read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS) is based on GRS. RA-GRS replicates your data to another data center in a secondary region, and also provides you with the option to read from the secondary region. With RA-GRS, you can read from the secondary region regardless of whether Microsoft initiates a failover from the primary to secondary region.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/bs-cyrl-ba/azure/storage/blobs/data-lake-storage-quickstart-create-account https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/common/storage-redundancy-grs