Given the following routing table:
How would an outgoing packet to the destination 192.168.2.150 be handled?
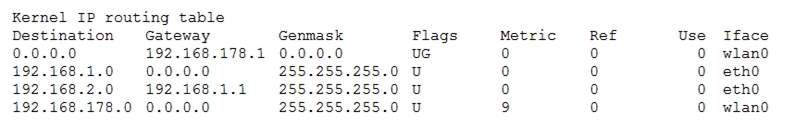
Given the following routing table:

How would an outgoing packet to the destination 192.168.2.150 be handled?
To determine how an outgoing packet to the destination 192.168.2.150 would be handled, we need to inspect the routing table. The routing table lists routes based on their destination network, gateway, netmask, and the interface (Iface) they should use. In this case, the routing entry for the destination network 192.168.2.0/24 (which includes 192.168.2.150) has a gateway of 192.168.1.1 and is associated with the eth0 interface. Therefore, the packet would be passed to the router 192.168.1.1 on eth0.
A is the answer 0.0.0.0 is a route to any network G flag indicates a gateway
D is correct This routing table is about a router/gateway with ethernet (eth0) and wifi (wlan0) interface. network 192.168.178.0 is connected via interface wlan0 to default gateway 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 is connected via interface eth0 to default gateway 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.2.0 is connected via interface eth0 to gateway 192.168.1.1 (on network 192.168.1.0) -----> then outgoing packet to reach 192.168.2.150 on network 192.168.2.0 will passed to gateway 192.168.1.1 -------> answer D
Proved in a lab on virtual box with several vm's in different segments: localhost:~ # route Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface default 192.168.1.254 0.0.0.0 UG 600 0 0 wlan0 10.10.20.0 192.168.56.201 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 vboxnet1 172.17.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 docker0 172.18.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 br-2d142c106ac3 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 600 0 0 wlan0 192.168.49.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 br-38c8ba0fd0af 192.168.56.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 vboxnet1 192.168.57.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 vboxnet0 localhost:~ # traceroute 10.10.20.1 traceroute to 10.10.20.1 (10.10.20.1), 30 hops max, 60 byte packets 1 192.168.56.201 (192.168.56.201) 4.347 ms 4.325 ms 4.308 ms 2 10.10.20.1 (10.10.20.1) 5.540 ms 5.549 ms 5.529 ms Destination IP 10.10.20.1 would represent the IP of option D
D is correct, because route is defined
D is correct because 192.168.2.0 route is "smaller" than 0.0.0.0 so the smaller route gets in first.
man route Flags Possible flags include U (route is up) H (target is a host) G (use gateway) R (reinstate route for dynamic routing) D (dynamically installed by daemon or redirect) M (modified from routing daemon or redirect) A (installed by addrconf) C (cache entry) ! (reject route)
Correct Answer is D. 192.168.2.0/24 is a static route and it is reached passing 192.168.1.1 via eth0. In routing table any static route (by default) is checked before default gateway . Default gateway will be hited once no match criteria will be found in the routing table .
Correct Answer is D.
D is Correct. 0.0.0.0/0 Matches the IP 192.168.1.0/24 no Match 192.168.2.0/24 Matches the IP -> this Route is used, becaus the Netmask on this Route is more precise, than that of the default Route. 192.168.178.0/24 no Match