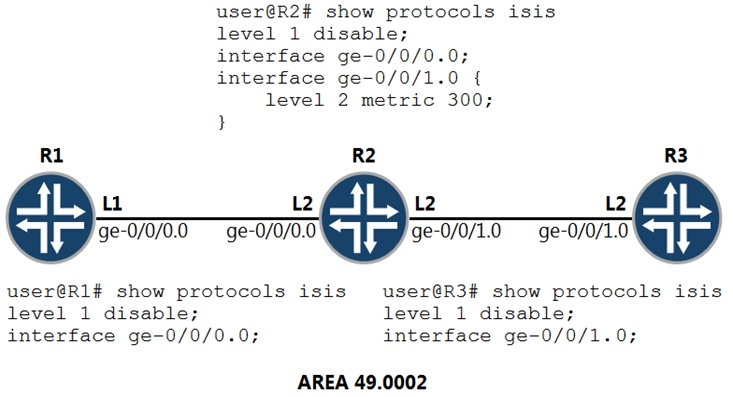
Referring to the exhibit, what will the IS-IS cost be for R3 to reach R1?

Referring to the exhibit, what will the IS-IS cost be for R3 to reach R1?
The IS-IS cost for R3 to reach R1 is 20. In IS-IS, the metric calculation is based on the cost of the outgoing interfaces along the path. The default metric for each interface is 10, and R2's configuration indicates that its interfaces have not been modified beyond the default value except for the specific condition where wide-metric is not enabled. Therefore, the cost for R3 to reach R1 is calculated as follows: the cost from R3 to R2 is 10 and from R2 to R1 is also 10, resulting in a total cost of 20.
The correct answer is "C" 20 The ISIS metric calculation is based in the outgoing interfaces of the routing path
And since the default metric is 10, so, 10+10=20
This is "C". I confirmed it vMX and metric was 20.
Yes, confirmed too in lab
Answer is B (73). lab@vMX03> show route 10.0.0.3 table PE1 PE1.inet.0: 5 destinations, 5 routes (5 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 10.0.0.3/32 *[IS-IS/18] 00:03:13, metric 73 > to 10.0.1.1 via lt-0/0/10.1
it is calculated with the outgoing interface of the router.
"D" 310 Default metric is 10 but the middle's router is set to 300 so would be 300+10=310
nm "B" With "wide-metrics-only" not configured the maximum metric of the outgoing interface is limited to 63 so 63+10=73 "D" would only be correct if the "wide-metrics-only" command were present. "C" would only be correct if R2's G0/0/1 interface metric wasn't set to 300.
"C" final answer, cost is calculated via outbound interfaces G0/0/1.0 is not an outbound interface...wish I could delete these but at least this lets know why it's C...
C = correct. ISIS advertises it metric in TLV, without "wide-metric-only" this is maximum 63. so R2 advertises its metric to R3. metric = 300, capped to 63 maximum metric from R1 > R2 = 10 (default), makes total 73.
"C" is the right one, cause they are asking about metric from R3 to R1. we have "R3 ge-0/0/1.0 (10) + R2 ge-0/0/0.0 (10) = 20 If they ask about metric from R1 to R3, 300 metric on R2 is ignored because wide-metric is not enable so the metric would be 73. R1 ge-0/0/0.0 (10) + R2 ge-0/0/1.0 (63) = 73
C 20 is correct labbed it up. Cost is of outgoing interfaces of the packetpath, or incoming interfaces where the router receives the LSP and add’s the metric of that interface.
Don't be confused with another similar question. In this case metric is 20.
C is the correct answer root@vMX-3> show route 1.1.1.1 inet.0: 6 destinations, 6 routes (6 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 1.1.1.1/32 *[IS-IS/18] 00:01:24, metric 20 > to 10.1.0.5 via ge-0/0/1.0
C 73 is correct
Correct answer is 73. Because Metric calculation on OSPF/ISIS is always added in inbound direction. Only difference is OSPF add Metrc-1 and ISIS add Metric-10 by default.
Also in this case, wide-metric is not enabled.... so 300 is converted into 63 as default.
ISIS uses cost of outgoing interface metric—Metric value. Range: 1 through 63, or 1 through 16,777,215 (if you have configured wide metrics) Default: 10 (for all interfaces except lo0), 0 (for the lo0 interface)
B is correct. The maximum metric of a narrow metric is 63, them the metric is 63 + 10.