Click the Exhibit button.
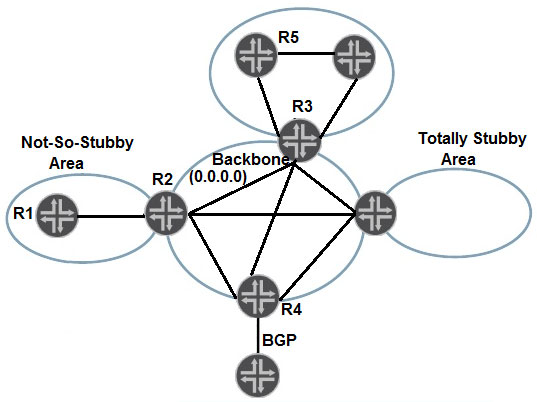
Referring to the exhibit, how is R5 able to learn the networks that exist within the NSSA?
Click the Exhibit button.

Referring to the exhibit, how is R5 able to learn the networks that exist within the NSSA?
R5 learns the networks within the NSSA from Type 3 LSAs advertised by R3. This occurs because R2, which is the Area Border Router (ABR) between the NSSA and the backbone area, creates Type 3 Summary LSAs for internal OSPF routes learned within the NSSA. These Type 3 LSAs are then flooded into the backbone area. R3, which is connected to both the backbone and the area containing R5, re-advertises these Type 3 LSAs into the area containing R5, thereby allowing R5 to learn about the networks in the NSSA.
B is correct. The flooding scope of Type-3 LSA is a single area.
Stub areas (in this case NSSA) influence which LSA will be allowed within that area. However, other areas will learn about OSPF internal networks of NSSA area via SLA type 3. R2 as ABR creates LSA type3 and R3 will recreate those LSAs and advertise into area where R5 is, so correct answer should be B.
Think B is correct!
Think A is correct
A is correct! R2 is going to create a Type 3 summary LSA and flood it into area 0. This LSA will flood into all the other areas of our OSPF network. This way all the routers in other areas will know about the prefixes from other areas. https://networklessons.com/ospf/ospf-lsa-types-explained
I think R2 will convert LSA7 into LSA5 and flood into area 0. And R3 will floor those route as LSA3. So B should be the correct answer.
Isn't A the right answer?
R5 is a no-backbone area. I also think is A https://www.juniper.net/documentation/images/g200034.png
Do not Approve! is not type 3 ... type 5!
LSA7 or LSA5 is only for redistribute routes. LSA3 will be for all internal routes.. if not cli was added for send only default , R5 will learn them as LSA3 from R2 LSA TYPES: Type 1 – Router LSA: The Router LSA is generated by each router for each area it is located. In the link-state ID you will find the originating router’s ID. Type 2 – Network LSA: Network LSAs are generated by the DR. The link-state ID will be the interface IP address of the DR. Type 3 – Summary LSA: The summary LSA is created by the ABR and flooded into other areas. Type 4 – Summary ASBR LSA: Other routers need to know where to find the ASBR. This is why the ABR will generate a summary ASBR LSA which will include the router ID of the ASBR in the link-state ID field. Type 5 – External LSA: also known as autonomous system external LSA: The external LSAs are generated by the ASBR. Type 6 – Multicast LSA: Not supported and not used. Type 7 – External LSA: also known as not-so-stubby-area (NSSA) LSA: As you can see area 2 is a NSSA (not-so-stubby-area) which doesn’t allow external LSAs (type 5). To overcome this issue we are generating type 7 LSAs instead.
ed@vMX_R2# run show ospf database OSPF database, Area 0.0.0.1 Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Router *2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 0x8000000f 1737 0x20 0xcb4 36 Router 4.4.4.4 4.4.4.4 0x8000000e 396 0x28 0x2067 48 Network 10.0.24.4 4.4.4.4 0x80000007 396 0x28 0xf9e5 32 NSSA 10.0.44.252 4.4.4.4 0x8000000b 656 0x28 0x3309 36 OSPF database, Area 0.0.0.2 Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Router 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 0x8000001a 1006 0x22 0x8c3c 60 Router *2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 0x80000010 2337 0x22 0xd9fa 48 Summary *2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 0x80000009 337 0x22 0xe044 28 Summary *4.4.4.4 2.2.2.2 0x80000005 1337 0x22 0xfa1b 28 Summary *10.0.24.0 2.2.2.2 0x80000019 737 0x22 0xf5fa 28
in thus scenario tested for network 4.4.4.4 yes - LSA 3 Summ
AREA 0 omitted from the output
ed@vMX-PE1# run show ospf database OSPF database, Area 0.0.0.2 Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Router *1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 0x8000001a 1449 0x22 0x8c3c 60 Router 2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 0x80000010 2782 0x22 0xd9fa 48 Summary 2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 0x80000009 782 0x22 0xe044 28 Summary 4.4.4.4 2.2.2.2 0x80000005 1782 0x22 0xfa1b 28 Summary 10.0.24.0 2.2.2.2 0x80000019 1182 0x22 0xf5fa 28 OpaqArea*1.0.0.1 1.1.1.1 0x80000008 438 0x22 0x22fd 28 OpaqArea 1.0.0.1 2.2.2.2 0x80000008 982 0x22 0x26f1 28 OpaqArea*1.0.0.3 1.1.1.1 0x80000005 2426 0x22 0x2520 136 OpaqArea 1.0.0.3 2.2.2.2 0x8000000b 2982 0x22 0xa09e 136 OSPF AS SCOPE link state database Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Extern 10.0.44.252 2.2.2.2 0x80000005 1582 0x22 0xf160 36 [edit] ed@vMX-PE1#
Anyway, EXTERNAL routes injected by 4.4.4.4 will always LSA type 5 ed@vMX-PE1# run show ospf database external extensive OSPF AS SCOPE link state database Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Extern 10.0.44.252 2.2.2.2 0x80000005 1681 0x22 0xf160 36 mask 255.255.255.252 Topology default (ID 0) Type: 2, Metric: 20, Fwd addr: 4.4.4.4, Tag: 0.0.0.0 Aging timer 00:31:58 Installed 00:27:58 ago, expires in 00:31:59 Last changed 03:33:31 ago, Change count: 1 [edit] ed@vMX-PE1#
It's a little bit tricky, because without R2, R3 and R5 learn nothing. But as said by certman20, The flooding scope of Type-3 LSA is a single area, so R5 cannot receive any Type-3 LSA from R2. So B is the correct answer. Please update
B. R3 will receive Type-3 LSA from R2 and then will re-create Type-3 LSA for upper area.