Refer to the exhibit.
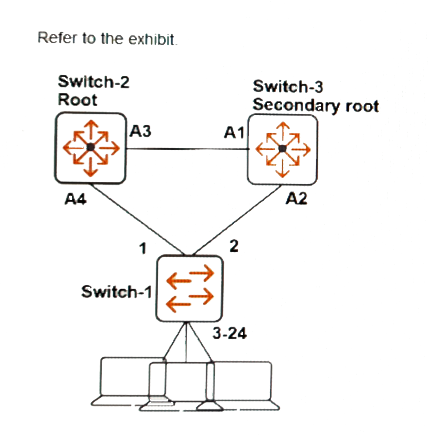
A network administrator wants to add the protections of root guard to the network. Based on the spanning tree topology, on which ports should the network administrator implement root guard?
Refer to the exhibit.

A network administrator wants to add the protections of root guard to the network. Based on the spanning tree topology, on which ports should the network administrator implement root guard?
Root guard should be implemented on ports that are not expected to be the path to the root bridge. In the given topology, Switch-1 should not try to become the root bridge. To prevent this, root guard should be enabled on the ports that connect Switch-1 to other switches, which are ports 1 and 2 on Switch-1. This ensures that Switch-1 does not receive a superior BPDU on these ports indicating it should become the root bridge.
Correct answer A. You configure root guard on ports that should never receive BPDUs with information about the root—in other words, designated ports and generally designated ports at the network edge.
A, it must be anable on edge ports.
The correct answer is "A". Root guard is enabled only on the egde ports, never on the ports that connect to the root bridge.
Root guard should be implemented on ports on the root switch pointing to distribution switches. Also on distribution switch ports pointing to access switches. In detail. It should be implemented on ports which should never become the root port. So to become the root port a superior BPDU is required. On Edge ports where only end systems connected no BPDU's are reveived or blocked by BPDU guard. So solution is C