A consultant is reviewing the following output after reports of intermittent connectivity issues:
Which of the following is MOST likely to be reported by the consultant?
A consultant is reviewing the following output after reports of intermittent connectivity issues:

Which of the following is MOST likely to be reported by the consultant?
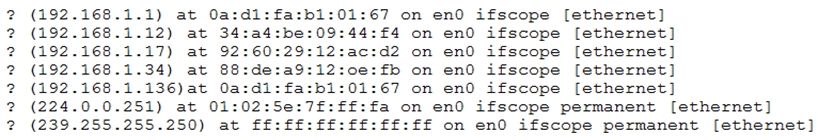
A device on the network has poisoned the ARP cache. The ARP table shows that the IP addresses 192.168.1.1 and 192.168.1.136 are both associated with the same MAC address (0a:d1:fa:b1:01:67). ARP cache poisoning is a type of attack where a malicious actor sends fake ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) messages onto a network. This results in the linking of an attacker's MAC address with the IP address of a legitimate computer or server on the network, causing network traffic to be misrouted.
D is correct
Option D, "A device on the network has poisoned the ARP cache," is the most likely issue to be reported by the consultant because it would cause the ARP cache to contain incorrect or malicious entries. ARP cache poisoning, also known as ARP spoofing, is a type of attack in which an attacker sends false ARP messages to a network, causing other devices to update their ARP caches with the attacker's false information. This allows the attacker to intercept or redirect network traffic.
D is the right answer. The IP address associated with the MAC was changed in the display.
D is correct
DDDDDDDDD
D. A device on the network has poisoned the ARP cache. Explanation: • ARP Cache Poisoning: The ARP table shows that the IP address 192.168.1.1 and 192.168.1.136 are associated with the same MAC address (0a:d1:fa:b1:01:67). This indicates that an ARP cache poisoning attack might be taking place, where a malicious device is sending spoofed ARP messages to associate its MAC address with the IP address of another device, causing network traffic to be misrouted.
2 IPS have the same MAC address.
The fact that there are multiple entries for the same MAC address (0a:d1:fa:b1:01:67) indicates that there is an issue with the ARP cache. Specifically, it appears that one device (with MAC address 0a:d1:fa:b1:01:67) is claiming to be multiple IP addresses on the network (192.168.1.1 and 192.168.1.136). This is an example of ARP cache poisoning, where a device sends fake ARP messages in order to associate its own MAC address with the IP address of another device on the network.
Multicast IP address with layer two broadcast? Wrong Multicast Group
I'm changing to D
look at the mac on the first multicast group that's wrong. My fist exp is wrong this one is right.....
D because of the multiple MAC address on the IP.
? (192.168.1.1) at ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff on en0 ifscope permanent [ethernet] This is an output of the 'arp -a' command, which shows the IP address (192.168.1.1), MAC address (ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff), network interface (en0) and scope (ethernet) information for the device on the local subnet. This indicates that the address resolution protocol (ARP) could not resolve the target's IP address to a valid MAC address.
D is correct answer