Refer to the exhibit.
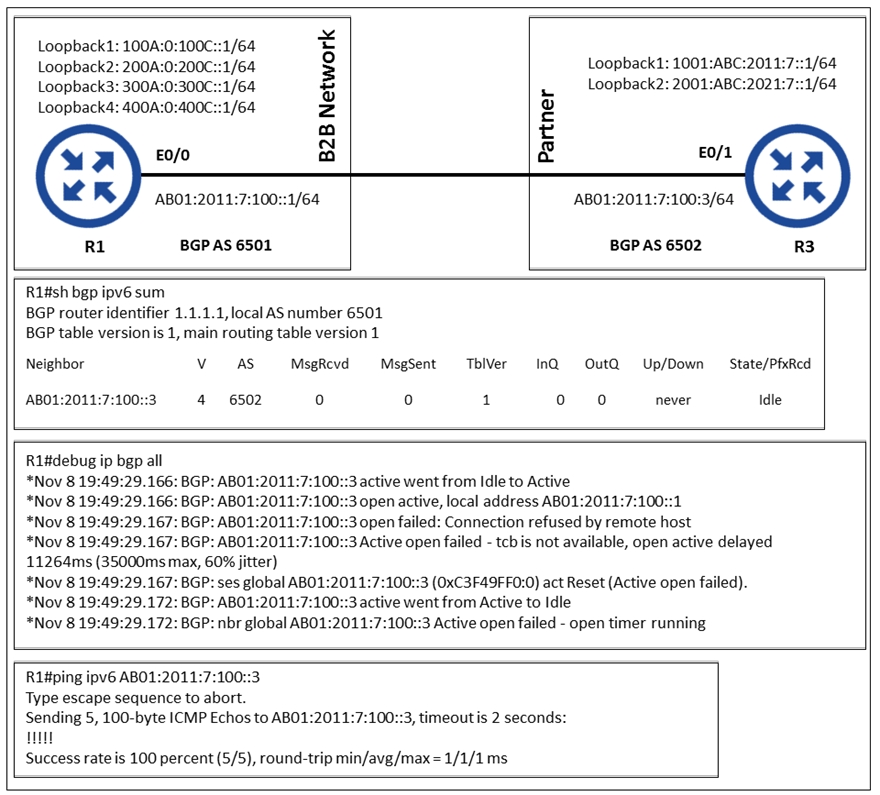
An engineer configured BGP between routers R1 and R3. The BGP peers cannot establish neighbor adjacency to be able to exchange routes.
Which configuration resolves this issue?
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer configured BGP between routers R1 and R3. The BGP peers cannot establish neighbor adjacency to be able to exchange routes.
Which configuration resolves this issue?
The BGP peers cannot establish neighbor adjacency because the remote router (R3) needs to activate the neighbor in address-family IPv6 unicast by running the 'neighbor <neighbor_IP> activate' command. This configuration ensures that the BGP session can be established, as indicated by the 'Connection refused by remote host' message in the debug output. Activating the neighbor on R3 will resolve the issue and allow the BGP peers to exchange routes.
B is the correct answer. As it states in the debug "Connection refused by remote host". Extra step needed on the remote router (R3) which is to activate the neighbor in address-family ipv6 unicast and run the "neighbor <neighbor_IP> activate" command.
The correct answer is: B
In the output you can see that R1 Neig session to R2 is active, but the R2 IP is rejection the connection, therefore you need to activate the neighbor connection on router 2
Labed it, answer is B
Tested on GNS3, it's B
It's B 4 sure
I just testes this scenrio on GNS3, and B is the correct answer
The given answer is correct, because the pong show that the R3 responded, which meant the configuration is correct, then we must look at R1 to see what chase the issue
B is the correct