An engineer configured access list NON-CISCO in a policy to influence routes.
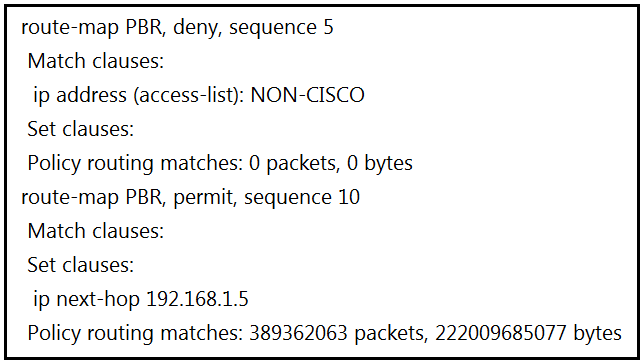
What are the two effects of this route map configuration? (Choose two.)
An engineer configured access list NON-CISCO in a policy to influence routes.

What are the two effects of this route map configuration? (Choose two.)
The route map configuration includes two sequences: sequence 5 and sequence 10. Sequence 5 denies packets that match the NON-CISCO access list, meaning these packets will be forwarded using the normal route lookup. Since the policy routing matches show 0 packets for sequence 5, no packets match this clause. Sequence 10 permits packets that do not match sequence 5 and sets the next hop to 192.168.1.5. Therefore, the packets that do not match the NON-CISCO access list are evaluated by sequence 10 and forwarded to the specified next hop. The correct answers are that packets are forwarded using normal route lookup if they match the NON-CISCO access list, and packets are evaluated by sequence 10 if they do not match the access list.
Seq 5 has a match ACL ---Deny Seq 10 has no match so Match Everything ---Permit So a packet ether it matched by ACL and forwarded using normal route lookup or does not get matched by ACL and evaluated by sequence 10. A , D
Make sense to go for A & D. Good job.
Yes. Makes sense. Thank you.
sorry for my poor english. seq 10 has no match. Can we say seq 10 do an "evaluate" ?
Since sequence 10 has no match condition that means that we can not evaluate according sequence 10 - So I guess the best options here are A & E
In my opinion B,D are correct answers. No any packets are evaluated by seq 5. It means that all packets are evaluated by seq 10. Because it has permit statement and no match any conditions all packets are routed to 192.168.1.5 by PBR. According to Cisco PBR command set-ip next hop explanation The set ip next-hop command verifies the existence of the next hop specified, and… ... if the next hop exists in the routing table, then the command policy routes the packet to the next hop. ... if the next hop does not exist in the routing table, the command uses the normal routing table to forward the packet. As we can see from output packets have been forwarded by sequence 10 and this is NO normal routing table. But here we need to be sure that 192.168.1.5 is default-gateway and it exists in the routing table.
"A" and "D" are right. If the packet match in ACL NON-CISCO, the route-map sequence 5 is set to deny it, but it is a PBR and not a filter, so the deny says to the packet follow the normal RIP lookup. Any other packet that does not match NON-CISCO ACL will match here, so it will forwarded to 192.168.1.5.
a and d, packet that are denied will not be drop but be process by normal routing table and packets that a matched will be evaluated and forwarded to the next-hop
C. Packets are dropped by the access list. D. Packets are evaluated by sequence 10.
In a route map context, ACLs do not drop packets. A is a better choice since is that is an 'effect' of the applied route-map config. If no set statements are made packets will be forwarded via the RIB
A and D
A & D are correct. either the packets are forwarded normally if they match the ACL else they are evaluated by sequence 10.
AD is optioN correct
Its A, D
Configuration: Deny Clause (sequence 5): Matches packets based on access-list NON-CISCO. Since the match count is zero, no packets have matched this clause. Permit Clause (sequence 10): Applies to all packets that do not match the deny clause. Sets the next-hop IP address to 192.168.1.5. A significant number of packets (389362063) match this clause. Effects: Packets not matching the deny clause (sequence 5) are evaluated by sequence 10. Packets are forwarded to the next-hop 192.168.1.5 as specified by sequence 10. Answer: D. Packets are evaluated by sequence 10. A. Packets are forwarded using normal route lookup. Given the absence of matches in the deny clause, packets proceed to be evaluated and forwarded as per the next hop specified in sequence 10.
The question is for packets that match ACL. For that packet, packets are evaluated in seq 5, and using normal route lookup. So my answare is A (normal route lookup) and E (not matched by sequence 10).
A &D As Jokerr mentioned. As we see we have hits only on route map 10 sequence, so we have D from that and what does this PBR sequence do? b If you do not match packets on a route-map during PBR (as sequence 10), PBR does not take any action on that packet, and is routed normally per the routing table/FIB/etc. So we have A from there. (https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/s/question/0D53i00000Kt0jACAR/policy-based-routing)
As ytsionis says because the route-map do not have an acl that is matching the traffic the PBR will not be applied to any prefix because without the ACL the PBR is not gonna math nothing
I will go with ae… I think the first deny in routemap already mean use routing table route in pbr. Pbr only execute upon a permit route map statement and has an implicit deny at the end. Since deny seq is before the permit, I think permit 10 won’t be executed.. but better verify with simulator
A E - because the seq 5 deny route map statement already mean the phr shall skipped to use routing table, so seq 10 is not evaluated. Tricky part is that it has matches for pbr matching because matching seq 5 is a match
A and D Any routes that match the NON-CISCO acl will be "denied", i.e. not processed by PBR and so will use the Routing Table (normal route lookup). =======> A Any routes that do NOT match the NON-CISCO acl are permitted by seq 10 and thus use the Next-hop of 192.168.1.5 ======> D
A & D are correct