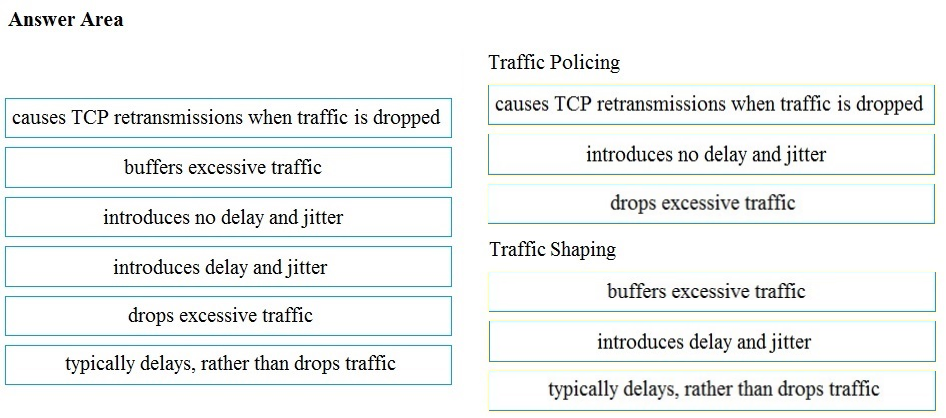
DRAG DROP -
Drag and drop the descriptions from the left onto the correct QoS components on the right.
Select and Place:

DRAG DROP -
Drag and drop the descriptions from the left onto the correct QoS components on the right.
Select and Place:

not correct, both answer with delay and jitter must be swap... (from Policing to shaping) https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/quality-of-service-qos/qos-policing/19645-policevsshape.html Shaping implies the existence of a queue and of sufficient memory to buffer delayed packets, while policing does not.
Just FYI for those wondering what chris7411 is talking about. It looks like admins fixed the answer so it is now correct
Traffic Policing causes tcp retransmitions Introduces no delay and jitter drops excessive traffic Traffic Shapping buffer excessive traffic Introduces delay and jitter typically delays , rather than drops traffic
Another logical reason that chris7411's answer is correct is that traffic shaping cannot both "introduce no delay" and "typically delay" simultaneously.
Traffic policing cause TCP retransmissions when traffic is dropped. introduce delay and jitter. drops excessive traffic. Traffic shaping buffers excessive traffic. introduces no delay and jitter. delays, rather than drops, traffic.
The provided answer seems correct. Policing drops packets which will cause TCP retransmission and no need for delay. Shaping buffers instead of dropping packets which will lead to queuing causing delays. Based on many comments, the provided answer is also valid.
Answer is Correct. Policing Advantages: - Drop (or remark) excess packets over the committed rates. Does not buffer. - Controls the output rate through packet drops. Avoids delays due to queuing. Policing Disadvantages: - Propagates bursts. Does no smoothing. - Drops excess packets (when configured), throttled TCP window sizes and reduces the overall output rate of affected traffic streams. Overly aggressive burst sizes can lead to excess packet drops and throttle the overall output rate, particularly with TCP-based flows. Shaping Advantages - Buffer and queue excess packets over the committed rates. - Controls bursts and smooths the output rate over at least eight-time intervals. Uses a leaky bucket to delay traffic, which achieves a smoothing effect. - Less likely to drop excess packets since excess packets are buffered. (Buffers packets up to the length of the queue. Drops can occur if excess traffic is sustained at high rates.) Typically avoids retransmissions due to dropped packets. Shaping Disadvantage: - Can introduce delay due to queuing, particularly deep queues.
DRAG AN DROP IT´S CORRECT BOOK: ccnp-350-401-official-cert-guide Chapter 14. QoS -Implement traffic policing to drop low-priority packets and allow high-priority traffic through. Then: " Drops excessive traffic" - Implement traffic shaping to delay , is not recommended for RTP,it relies on queuing that can cause jitter. Then: "introduces delay and jitter" whereby: traffic policing = "introduces no delay and jitter" -Shapers: Buffer and delay egress traffic rates ***deleted for space*** then: "Buffers excessive traffic" -Policers for incoming traffic ***deleted for space***. A downside of policing is that it causes TCP retransmissions when it drops traffic. the: "Cuase TCP retransmission when traffic is dropped" - Shapers are used for egress traffic ***deleted for space***. Shaping buffers and delays traffic rather than dropping it, and this causes fewer TCP retransmissions compared to policing. then: "typically delays ,rather than drops traffic"
Traffic Shaping according to the book: Implement traffic shaping to delay packets instead of dropping them since traffic may burst and exceed the capacity of an interface buffer. Traffic shaping is not recommended for real-time traffic BECAUSE IT RELIES ON QUEUING THAT CAUSE JITTER.
all is rite
given answer is correct
hint ~jitter & delay: packet gets neither delay nor jitter when it gets dropped
1,3,5 - TP 2,4,6 - TS
provided answer is correct
Shaping definitely introduces delay due to queuing.... So 'Introduces delay and jitter' should be under 'traffic shaping'..
Shaping places packets into queues when the actual traffic rate exceeds the traffic contract, which causes more delay, and more jitter. Policing when making a simple decision to either discard or forward each packet causes more packet loss, but less delay and jitter for the packets that do make it through the network
policing drops and shaping buffers the traffic
For traffic shaping, one says, "no delays", the other says, "typically delay". I am getting confused. For shaping, the traffic must be delayed