Refer to the exhibit.
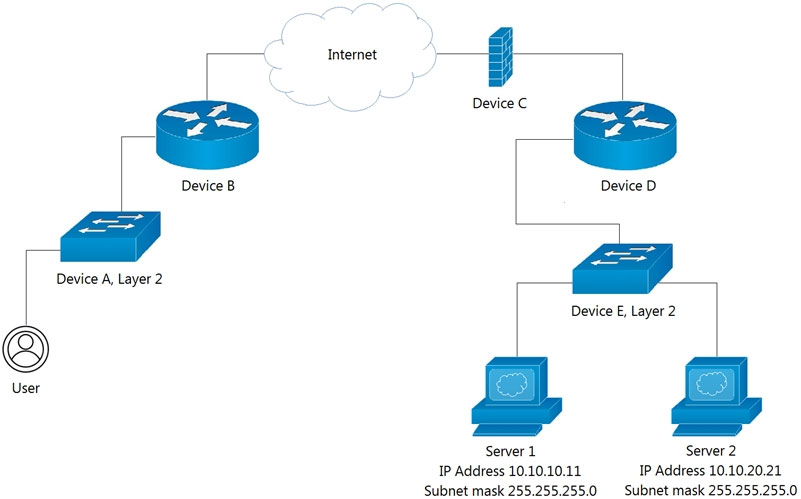
Which Device limits traffic between Server 1 and Server 2?
Refer to the exhibit.

Which Device limits traffic between Server 1 and Server 2?
Device D is the device that limits traffic between Server 1 and Server 2. This is because Server 1 and Server 2 are on different subnets (10.10.10.0/24 and 10.10.20.0/24, respectively). Routers, such as Device D, are designed to direct traffic between different subnets, thus serving as the gateway for communication between these servers. Without the router, packets from one subnet would not reach the other, thereby limiting traffic. This function cannot be performed by Layer 2 switches like Device E, which operate within a single broadcast domain and cannot route traffic between different subnets.
The question says "limits", for me that is the function of the L2 Switch, it separates traffic in different broadcast domains, whereas a router "forwards" traffic based on the routing table and the routing protocol. The answer for me is D - Device E Layer 2
Since servers are in different networks, they need a router to communicate. The router does not send the packets to the firewall because the next hop is on the same interface that connects down to the servers.
It allows the traffic, but limits it. Switch not doing any layer 3 function or trunking. Answer should be Device D router --> as it allows the traffic but limits it by not allowing broadcast network type
The packets will not go through the firewall. They would go to the router and it will decide what to do
The router is needed in order to let them communicate since they are on different subnets.
Device D
Network with VLAN When VLANs are implemented on a switch, the transmission of unicast, multicast, and broadcast traffic from a host in a particular VLAN, are limited to the devices present in the VLAN. So, i think is D. Device E , but the question is weird and freaky
this question appears in my exam, but with another sentence, up what device can comunicate the hosts? My answer was device switch
stupid question, because the firewall, router, and switch could be enabled with QoS to limit traffic to a destination device via layer-2 (switch) or layer-3 (router/firewall). Policy based routing could be configured on the router and is that a layer-3 switch?
The switch is just an L2 switch, it is not a multilayer switch. In order for the logical networks to communicate with each other a router is required. Again it is because they are in different logical broadcast domain and we require an L3 device to route traffic between domains. Multilayer L2/L3 switch is fine, but the one provided just L2 hence unable to route traffic between broadcast domains.
It cannot be device D. Both servers are on the SAME subnet, therefore Packets will NOT traverse the router. So the answer has to be D (switch). This could be done via VACLs, PVLANs, etc.
Answer C
The answer is C - Device D The question says "which device limits data BETWEEN the servers". Aka Server 1 is sending data to server 2, which device limits/blocks data between the two separate subnets? the Router!
D: The switch is the device that splits the network into multiple VLANs, thus limiting the communication The router will route between the VLANs and enable traffic
Switch E.
Switch(device E) 'limits' the traffic between server1 and server2. Router enables this traffic!
You could configure the firewall to limit traffic over a threshold, and you could configure QoS on the routers to limit traffic, and if that's a L3 switch, using QoS you could limit traffic from the source to the destination too. The question is bogus
Silly question.. it can also be B(the firewall) if both of the router's interface was configured as a trunk port.