Refer to the exhibit below.
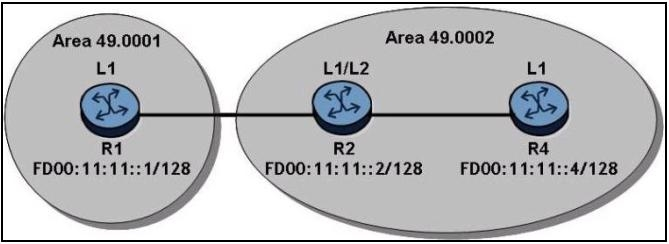
R1 distributes its loopbacks into IS-IS and globally routed addresses are configured as shown. How many routes will R4 have in its IPv6 route table?
Refer to the exhibit below.

R1 distributes its loopbacks into IS-IS and globally routed addresses are configured as shown. How many routes will R4 have in its IPv6 route table?
R4 will have 2 routes in its IPv6 route table. Since R1 is in a different area and is an L1 router, it does not form an adjacency with R2, which is an L1/L2 router in another area. As a result, R1's loopback address will not be propagated to R4. Therefore, R4 will only have routes to its own loopback address and the globally routed address of R2, totaling 2 routes.
c is correct
R2 + R4 globally routed addresses + default route to R2 = 3 routes
B. 2 correct. Because R1 and R2 can't handshark each other.
B. 2 correct. Because R1 and R2 cannot handshake each other.
@snowblack has a point. That is an L1 router from Area 49.001 connected to L1/L2 router in a different area.
R2+R4+Default Route = 3 routes
probably R1 is typing mistake , it must be L2 or L1/L2 router , also it doesnt effect the answer
The correct answer is 2, because there will be no adjacency or exchange between R1 and R2