Click the exhibit button.
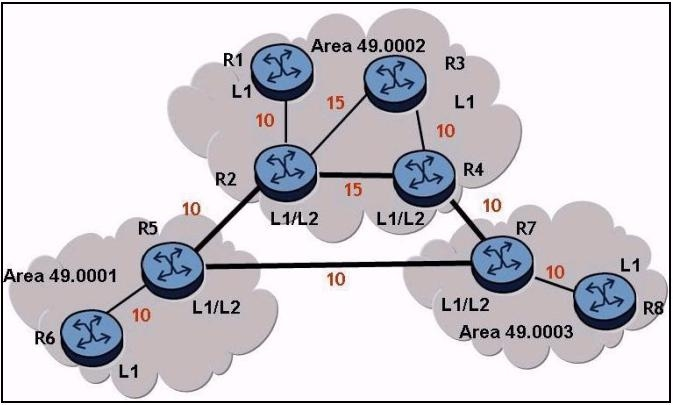
Given the diagram below, what path will traffic follow from router R6 to router R3, and from router R3 to router R6, if IS-IS is the routing protocol? The numbers beside the links are the metrics for that link.
Click the exhibit button.

Given the diagram below, what path will traffic follow from router R6 to router R3, and from router R3 to router R6, if IS-IS is the routing protocol? The numbers beside the links are the metrics for that link.
In IS-IS routing protocol, routers use metrics to determine the best path to reach the destination. For traffic from R6 to R3, the route R6-R5-R2-R3 is chosen because the total metric cost is 10 (R6-R5) + 10 (R5-R2) + 15 (R2-R3) = 35. For traffic from R3 to R6, the route R3-R2-R5-R6 is also chosen as R3 will use the same route in reverse to reach R6 due to the symmetrical nature of metric-based path selection, making the total metric cost 15 (R3-R2) + 10 (R2-R5) + 10 (R5-R6) = 35. Both directions follow the same path because they have the same cumulative metric cost.
I think Answer is D, As link cost between R2 and R3 is 15
Sorry answer C is correct
R3 has default route from R4 that has better metric than default route from R2. R4 has better metric over R7 than over R2 to R5. So C is correct.