After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You are designing an Azure SQL Database that will use elastic pools. You plan to store data about customers in a table. Each record uses a value for
CustomerID.
You need to recommend a strategy to partition data based on values in CustomerID.
Proposed Solution: Separate data into shards by using horizontal partitioning.
Does the solution meet the goal?
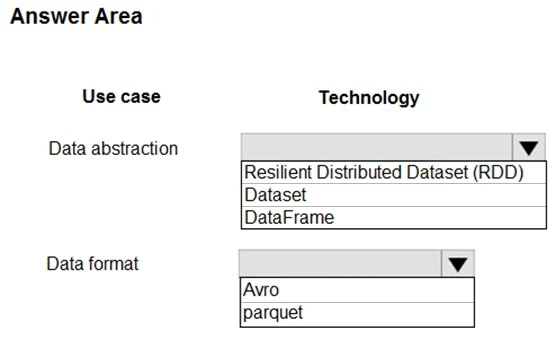
You are designing a data processing solution that will run as a Spark job on an HDInsight cluster. The solution will be used to provide near real-time information about online ordering for a retailer.
The solution must include a page on the company intranet that displays summary information.
The summary information page must meet the following requirements:
✑ Display a summary of sales to date grouped by product categories, price range, and review scope.
✑ Display sales summary information including total sales, sales as compared to one day ago and sales as compared to one year ago.
✑ Reflect information for new orders as quickly as possible.
You need to recommend a design for the solution.
What should you recommend? To answer, select the appropriate configuration in the answer area.
Hot Area:
You need to recommend a data storage solution that represents data by using nodes and relationships in graph structures.
Which data storage solution should you recommend?
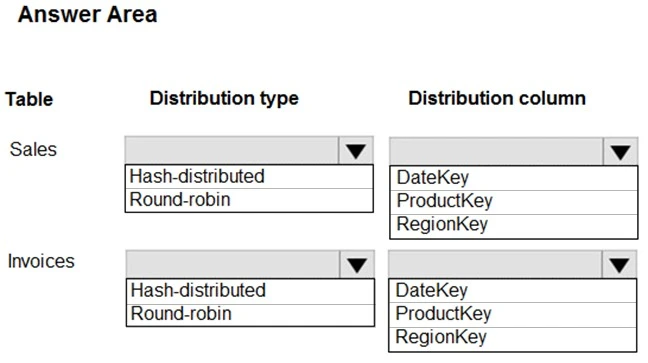
You have an on-premises data warehouse that includes the following fact tables. Both tables have the following columns: DataKey, ProductKey, RegionKey.
There are 120 unique product keys and 65 unique region keys.
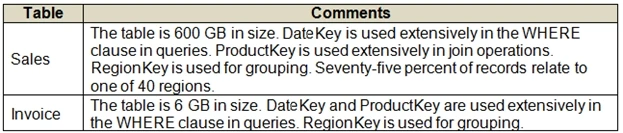
Queries that use the data warehouse take a long time to complete.
You plan to migrate the solution to use Azure Synapse Analytics. You need to ensure that the Azure-based solution optimizes query performance and minimizes processing skew.
What should you recommend? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
You need to recommend a data storage technology for the solution.
Which two technologies should you recommend? Each correct answer presents a complete solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.