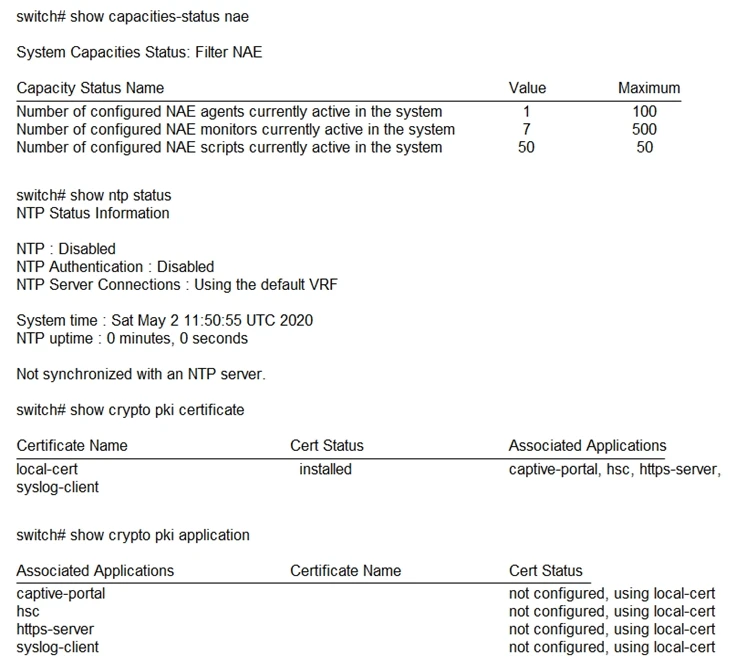
What should the engineer perform to fix this issue?

The issue at hand is that the AOS-CX switch has reached its maximum capacity for configured NAE scripts, as indicated by the capacity status showing 50 scripts currently active out of a maximum of 50. To resolve this issue, the engineer needs to remove a script that is no longer used before installing the new script. This will free up space and allow the new script to be added without exceeding the switch's capacity.
Community votes
No votes yet
To correctly identify a VLAN as a voice VLAN on an AOS-CX switch, you need to enter the VLAN configuration context and use the 'voice' command. The correct sequence is: Switch(config)# vlan
Community votes
No votes yet
To allow both VSX-capable core switches to process traffic sent to the default gateway in the campus VLANs, the administrator should implement the Active Gateway feature. In a VSX system, Active Gateway provides redundant default gateway functionality, where each switch in the VSX pair can act as an active default gateway for the VLAN using a shared virtual IP and virtual MAC address. This setup eliminates the need for traditional protocols like VRRP, which operate on an active-standby basis, whereas Active Gateway allows both switches to actively forward traffic.
Community votes
No votes yet
AOS-CX switches and Aruba Mobility Controllers use the same management protocol as Aruba APs, which is PAPI (UDP port 8211). The AOS-CX switches do not use IPSec for protection like the APs do for the PAPI connection between the AP and MC. Instead, optional MD5 HMAC protection can be implemented for PAPI communication between AOS-CX switches and MCs.
Community votes
No votes yet
IGMP must be enabled on all routed interfaces where multicast traffic will traverse. This ensures that the routers can participate in IGMP signaling and properly handle the multicast traffic, allowing them to manage the membership information of multicast groups and ensure efficient multicast data delivery across the network.
Community votes
No votes yet