When considering the functions of automation stitches, two key functionalities stand out. Firstly, an automation stitch configured to execute actions sequentially can indeed take parameters from previous actions as input for the current action, providing logical continuity and flexibility in automation workflows. Secondly, automation stitches can be created to run diagnostic commands and attach the results to an email message when CPU or memory usage exceeds specified thresholds, which is a valuable feature for proactive monitoring and alerting in network management. These functions clearly illustrate the capabilities of automation stitches in enhancing automated network operations.
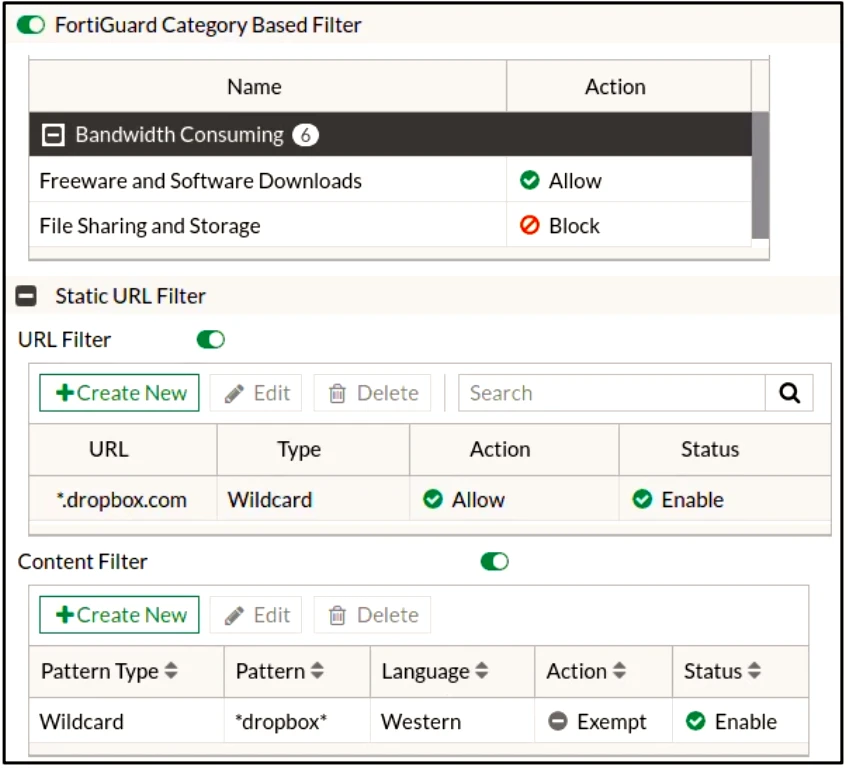
Which action will FortiGate take if a user attempts to access www.dropbox.com, which is categorized as File Sharing and Storage?
The FortiGate web filter processes the URL filter first, followed by the FortiGuard category-based filter. In this scenario, the URL filter allows access to *.dropbox.com, which means the connection is passed to the next filtering step. The FortiGuard category-based filter then checks the URL and finds that it falls under the File Sharing and Storage category, which is set to block. Consequently, FortiGate will block the connection based on the FortiGuard category-based filter configuration.
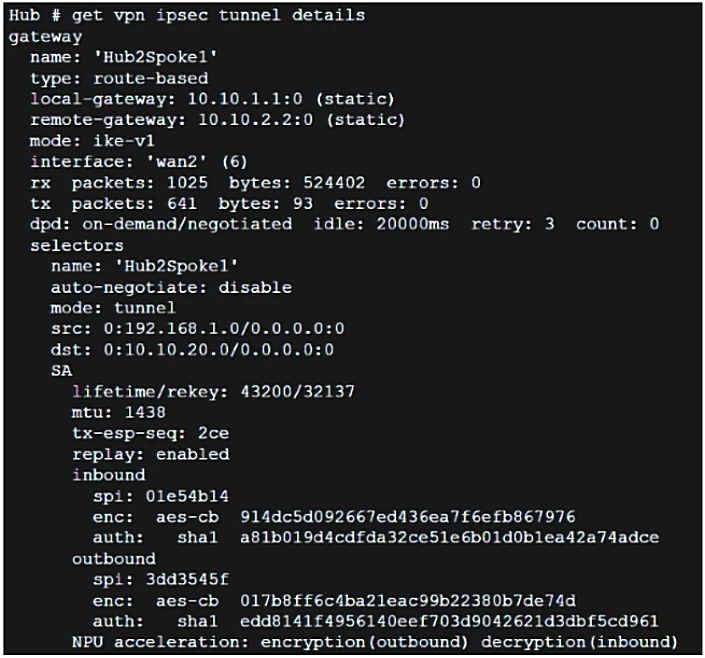
Based on the output, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
Anti-replay is indicated as enabled in the output under the field 'replay: enabled'. The npu_flag for this tunnel being 02 means that the inbound IPsec SA is copied to NPU, as suggested by the options. The given output specifies the functions of NPU acceleration for encryption (outbound) and decryption (inbound), which matches the definition of npu_flag 02.
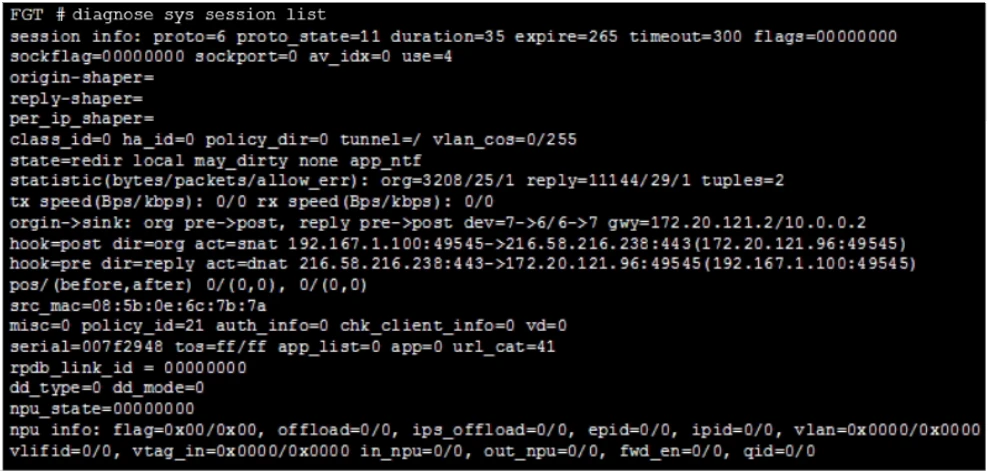
Which statement about FortiGate behavior relating to this session is true?
The session table entry indicates that the FortiGate is performing security profile inspection using the CPU. This can be deduced from several pieces of information in the session table. Specifically, 'offload=0/0' under the 'npu info' section means that the session is not being handled by the NPU (Network Processing Unit) but rather by the CPU. Additionally, 'proto_state=11' indicates inspection, as the first digit representing the server-side state is not zero, which implies inspection. Together, these details confirm that the FortiGate is inspecting the session using the CPU. Therefore, the correct answer is that FortiGate is performing security profile inspection using the CPU.
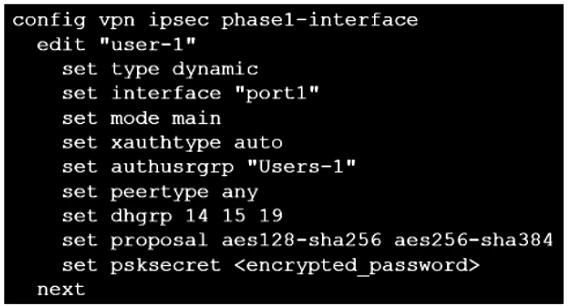

An administrator has configured two VPNs for two different user groups. Users who are in the Users-2 group are not able to connect to the VPN. After running a diagnostics command, the administrator discovered that FortiGate is not matching the user-2 VPN for members of the Users-2 group.
Which two changes must the administrator make to fix the issue? (Choose two.)
To resolve the issue where Users-2 group members are not able to connect to the VPN, the administrator must set up specific peer IDs on both VPNs and change to aggressive mode on both VPNs. These changes facilitate the correct matching of VPN configurations in scenarios with multiple dial-up VPNs using the same local gateway and sharing similar security association settings.