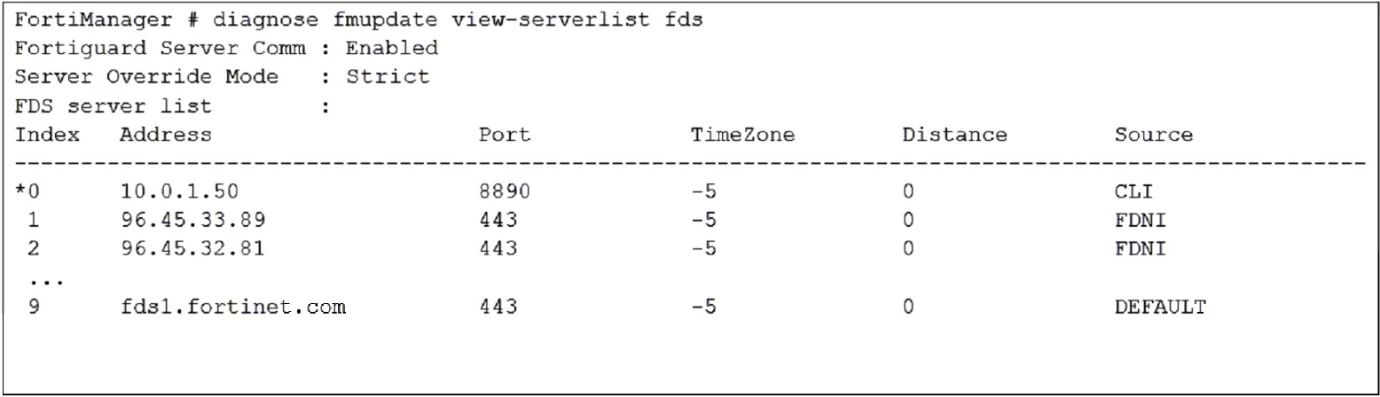
How will FortiManager try to get updates for antivirus and IPS?

When the Server Override Mode is set to Strict, FortiManager will only try to get updates from the configured override servers. In this case, the override server IP address 10.0.1.50 is the only one listed under the CLI source type, indicating it has been manually configured. Therefore, FortiManager will get updates only from the IP address 10.0.1.50.
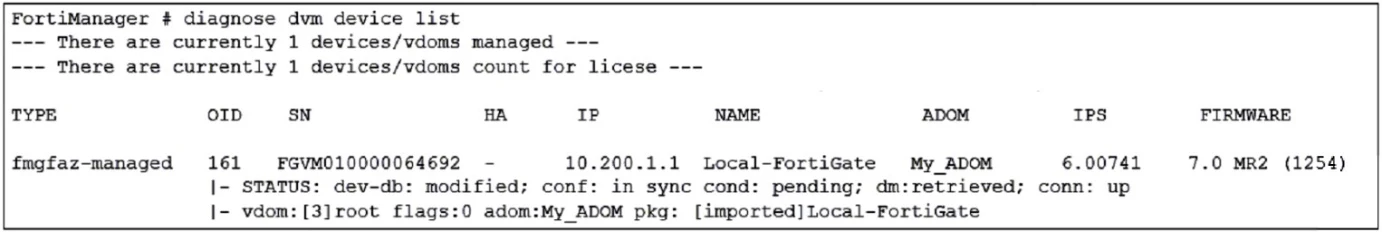
The output indicates that the FortiGate configuration is in sync, as suggested by the 'conf: in sync' status. However, the 'dev-db: modified' and 'cond: pending' status suggest that the latest revision history for the managed FortiGate does not match the device-level database. This implies that changes have been made but are pending installation, which means the changes have not yet been applied to the FortiGate device configuration.
To enable Management Extension Applications (MEA) on FortiManager, it is necessary to ensure that the ports to the Fortinet registry are open, allowing the connection and download of MEAs. Additionally, the administrator must have the super user profile to configure and manage these settings.

Based on the provided configuration, the workspace mode is set to normal in FortiManager. This setting means that changes are not automatically submitted or installed; instead, they need to be reviewed and installed manually. If an administrator's session is closed ungracefully, the ADOM remains locked until the session times out, ensuring the ADOM is not left in an indeterminate state. Additionally, the same administrator can lock more than one ADOM at the same time, allowing concurrent modifications across different ADOMs. Therefore, the correct answers are B and C.
When a new policy package is created, FortiManager automatically assigns the global policy package to the new policy package. This is because the global policy package is already assigned to the ADOM, and FortiManager applies it by default to any new policy packages created within that ADOM.