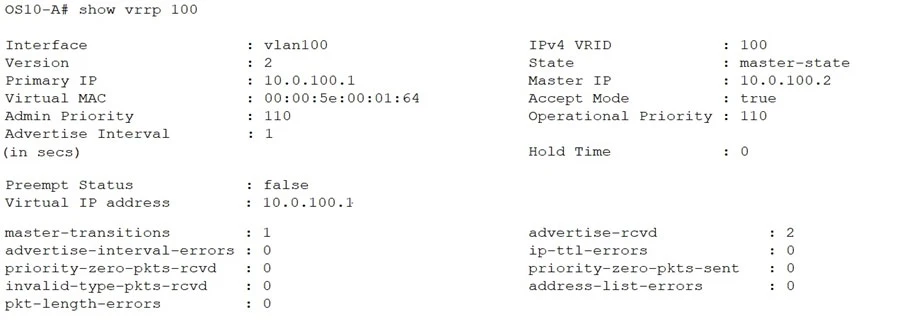
The suggested answer is C.
The VRRP state of OS10-A after a router with a default VRRP admin priority with VRID100 comes online would be 'backup-state.' This is because the existing router, OS10-A, has an admin priority of 110. In VRRP, the router with the highest priority becomes the master. The default VRRP priority is typically 100, which is lower than 110. However, the key detail here is that the 'Preempt Status' is set to 'false,' meaning OS10-A will not take over as master if another router is already master, even if the other router has a lower priority. Hence, OS10-A will stay in 'backup-state.'