Which of the following must the company do to ensure GDPR compliance? (Choose two.)
To ensure GDPR compliance when deploying a global service, companies must inform users regarding what data is stored. This is crucial as GDPR mandates transparency about data processing activities, meaning users need to be aware of what data is collected, how it will be used, and who it will be shared with. Additionally, companies must provide data deletion capabilities, as individuals have the right to request that their personal data be erased under certain conditions. This aligns with GDPR's principle of 'the right to be forgotten'. Opt-in/out capabilities for marketing messages, while important, are not as critical as data transparency and deletion capabilities under GDPR.
Community votes
No votes yet
Which of the following is the MOST likely cause?
The most likely cause for specific traffic not being logged and no visibility from the WAF for the web application is an expired certificate on the WAF. When the certificate on the WAF expires, it causes issues with the inspection of HTTPS traffic. Typically, WAFs inspect encrypted traffic (HTTPS) by decrypting it using valid certificates. If the certificate is expired, the WAF cannot decrypt the traffic, resulting in lack of logging and visibility. The other options do not impact logging and visibility in this manner.
Community votes
No votes yet
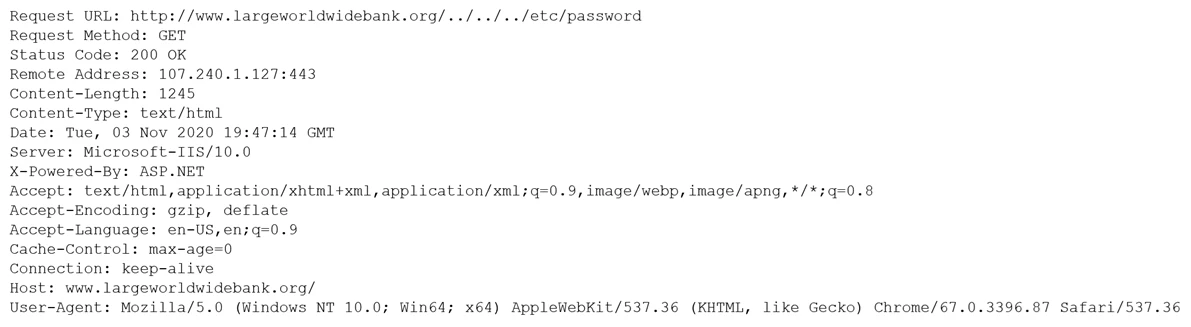
Which of the following would BEST mitigate this type of attack?
The output indicates an attempt to access a sensitive file, such as "/etc/password", using a directory traversal attack. This attack type exploits insufficient validation of user-supplied input, specifically crafted URLs that access directories other than the intended one. Placing a Web Application Firewall (WAF) inline is the best mitigation strategy for such attacks. A WAF can inspect and filter HTTP traffic, blocking malicious requests aimed at exploiting vulnerabilities in the web application, thus protecting against directory traversal attacks.
Community votes
No votes yet
Key distribution involves the process of securely delivering cryptographic keys to their intended recipients, such as a CASB or third-party entity. This ensures that the recipients can access the keys for encryption and decryption purposes. The term focuses on the act of delivering the keys rather than storing or recovering them.
Community votes
No votes yet
✑ Supporting MFA against on-premises infrastructure
✑ Improving the user experience by integrating with SaaS applications
✑ Applying risk-based policies based on location
✑ Performing just-in-time provisioning
Which of the following authentication protocols should the organization implement to support these requirements?
OAuth and OpenID Connect are modern authentication protocols suitable for integrating with SaaS applications and providing a seamless user experience. OAuth allows for secure authorization by enabling third-party applications to access resources without sharing user credentials, which supports the integration with SaaS applications and risk-based policies. OpenID Connect, built on top of OAuth, adds an identity layer to authenticate users, making it suitable for just-in-time provisioning and multi-factor authentication (MFA). Therefore, these protocols align with the organization's objectives of supporting MFA, integrating with SaaS applications, applying risk-based policies, and enabling just-in-time provisioning.
Community votes
No votes yet