When handling a ransomware infection, the technician's first priority should be to prevent the malware from spreading or causing further damage. Quarantining the system is the most appropriate initial step. This will isolate the infected machine from the network and other devices, helping to contain the threat and limit its potential impact. Once the system is quarantined, further steps such as scanning and removing the malware, disabling System Restore, and scheduling automated malware scans can be taken.
To ensure data is secure if a smartphone is lost or stolen, the best solution is the ability to remotely wipe the device. Remote wipe allows the company to erase all data on the smartphone from a distance, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information. While other options like screen locks and locator applications provide some level of security, they do not guarantee that the data will remain inaccessible if someone gains possession of the device and has the technical skills to bypass these measures. Anti-malware is useful for protecting against software threats but does not address the issue of physical loss or theft. Remote wipe is the only option that ensures the data can be completely removed from the device, thereby safeguarding it from unauthorized access.
The user is experiencing random advertisement notifications in the Action Center that are coming from a web browser. Disabling the browser from sending notifications to the Action Center is the best solution because it directly addresses the source of the issue. The advertisements are seen in the Action Center because the browser is configured to send notifications there. By disabling this feature, the user will no longer receive these advertisement notifications. This approach is more efficient than running an antivirus scan, which might not address the specific issue of browser notifications, or disabling all Action Center notifications, which could suppress important alerts from other applications.
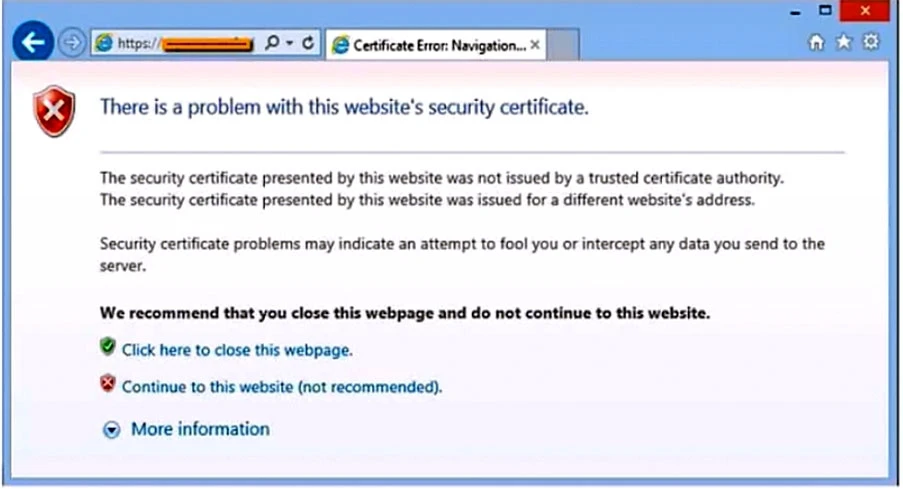
The CFO then reported the incident to a technician. The link is purportedly to the organization's bank. Which of the following should the technician perform FIRST?
The correct first action the technician should perform is to instruct the CFO to exit the browser. The security certificate error indicates that the website's security cannot be trusted, potentially due to it being a fraudulent or malicious site. Closing the browser immediately helps prevent any potential security threat or data compromise. Once the immediate threat is mitigated, the technician can take further steps to investigate the issue, such as updating the browser's Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) or contacting the involved parties. However, the immediate priority is to ensure the CFO's system is not exposed to any potential harm.
The most effective way to check other machines on the network for an unknown threat is to provide a sample of the executable to the antivirus vendor. The vendor can analyze the sample, develop detection signatures, and update their antivirus definitions. This ensures that all machines running the updated antivirus software will be able to detect and handle the threat. This method is comprehensive and efficient, as it leverages the expertise and resources of the antivirus vendor to protect all machines in the network.