Software-defined networking (SDN) fundamentally shifts networking by abstracting the control plane from the data plane, enabling centralized management. SDN is built upon a robust software stack, which provides flexibility and programmability (B). Additionally, SDN allows for automation through expressed intent to a software controller, reducing the need for manual device-by-device configurations (D). Traditional networks, by contrast, often require significant physical hardware resources and tightly coupled control and data planes, which are less flexible and harder to manage at scale.
A.

B.

C.

D.

The correct set of commands to initialize a Git repository, add a file, commit the changes, link it to a remote repository, and push the initial commit would be as follows: First, initialize a new Git repository with `git init`. Next, add the `device_status.py` file using `git add device_status.py`. Then, commit the changes with a message using `git commit -m "Initial Revision"`. Add the remote repository using `git remote add origin https://git.cisco.com/python_programmer/device_status.git`. Finally, push the changes to the remote repository with `git push -u origin master`. Therefore, the closest correct answer is option A, but there is a typo in the filename. The correct sequence should be as follows: `git init`, `git add device_status.py`, `git commit -m "Initial Revision"`, `git remote add origin https://git.cisco.com/python_programmer/device_status.git`, `git push -u origin master`.
Synchronous calls to APIs block until a response is returned from the server. This means the application will wait for the call to be completed before it can continue execution, adding perceived latency to the application if the data is not received promptly. Unlike asynchronous calls, which allow the application to proceed without waiting for the response, synchronous calls hold up the execution flow until the process is completed.

Refer to the exhibit. What is the result when running the Python scripts?
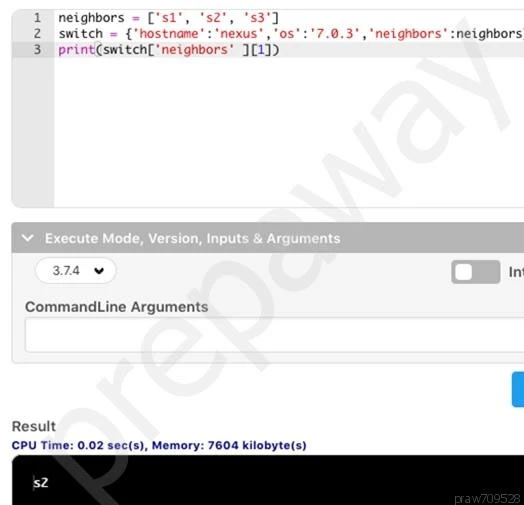 B
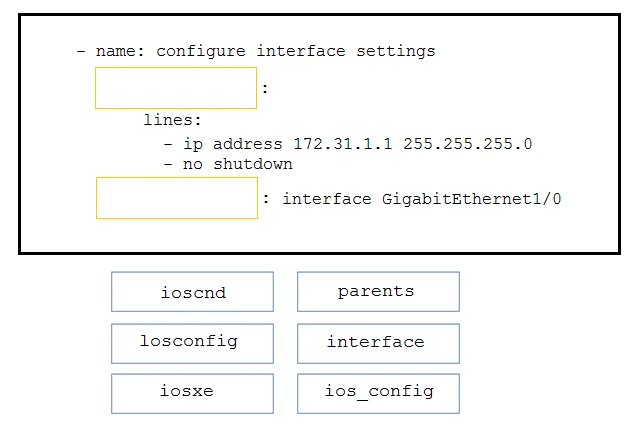
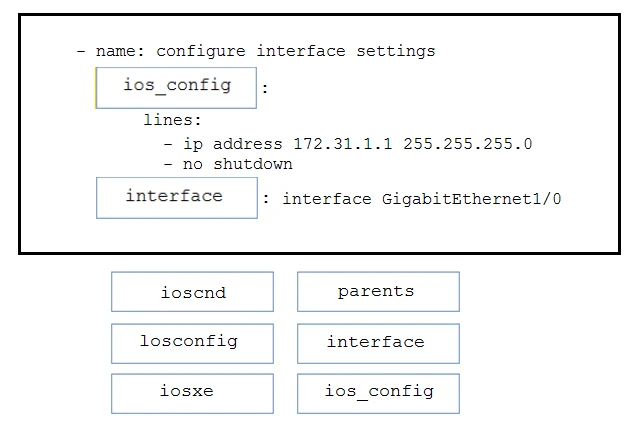
BDrag and drop the code from the bottom onto the box where the code is missing in the Ansible playbook to apply the configuration to an interface on a Cisco IOS
XE device. Not all options are used.
Select and Place: