EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) uses the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) to build its routing table. The DUAL algorithm ensures loop-free and efficient routing, making it central to EIGRP's operation.
The maximum number of routers that each OSPF area (including the backbone) should contain is generally recommended to be 50. This is to ensure efficient management and performance of the routing protocols within the area.
In general, any one router in an OSPF area should have no more than 60 neighbors to maintain efficient operations and minimize the workload during link-state changes.
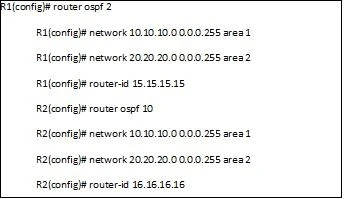
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the configuration, why are routers R1 and R2 not exchanging OSPF routes?
Routers R1 and R2 are not exchanging OSPF routes because the OSPF process numbers are different. In OSPF, routers with different process numbers will not form an adjacency and hence will not exchange routes. The process numbers (2 for R1 and 10 for R2) must be the same for OSPF neighbors to communicate.
An engineer can configure peer groups to simplify BGP neighbor statements and generate more efficient BGP peer updates. Peer groups allow the engineer to apply the same configuration parameters to multiple BGP peers, reducing redundancy and simplifying management. This approach streamlines the BGP configuration process by grouping multiple peers with similar characteristics, resulting in more organized and efficient configurations.