(e.g., which rack/port to connect).
What is the AWS-recommended procedure for providing this information?
When setting up an AWS Direct Connect connection, the recommended procedure is to create a new connection through your AWS Management Console. After you request the connection, AWS makes a Letter of Authorization and Connecting Facility Assignment (LOA-CFA) available to you to download. This LOA-CFA includes the necessary details such as rack and port information needed for the cross-connect. There is no need to create a support ticket or contact an AWS Account Manager directly for this process.
Community votes
No votes yet
The ELB is configured to use round robin, and sticky sessions are disabled. You have configured the NACLs and security groups to allow port 22 from your bastion host, and port 80 from 0.0.0.0/0. The client configuration is managed by each regional IT team.
Upon inspection you find that a large amount of requests from incorrectly configured sites are causing a single application server to degrade. The remainder of the requests are equally distributed across all servers with no negative effects.
What should you do to remedy the situation and prevent future occurrences?
To remedy the situation and prevent future occurrences, the best course of action is to update the security groups to only allow port 80 traffic to the application servers from the ELB. This ensures that all traffic is forced through the ELB, which distributes the requests evenly. By restricting direct access, incorrectly configured client applications cannot target a single application server directly, thereby avoiding degradation of individual servers. This approach mitigates the risk of public IPs being used to bypass the load balancer, which could cause similar issues in the future.
Community votes
No votes yet
According to the organization's security team, the VPN must meet the following requirements:
✑ AES 128-bit encryption
✑ SHA-1 hashing
✑ User access via SSL VPN
✑ PFS using DH Group 2
✑ Ability to maintain/rotate keys and passwords
✑ Certificate-based authentication
Which solution should you recommend so that the organization meets the requirements?
A third-party VPN solution deployed from AWS Marketplace is the correct choice. AWS hardware VPN solutions do not support SSL VPN for user access or certificate-based authentication. Additionally, AWS Site-to-Site VPN connections do not provide the ability to rotate keys and passwords, which is a security requirement. Third-party VPN solutions offer advanced features including AES-128 encryption, SHA-1 hashing, PFS with DH Group 2, user access via SSL VPN, the capability to maintain and rotate keys and passwords, and certificate-based authentication. These features make the third-party VPN solution from AWS Marketplace the best fit to meet all the specified requirements.
Community votes
No votes yet
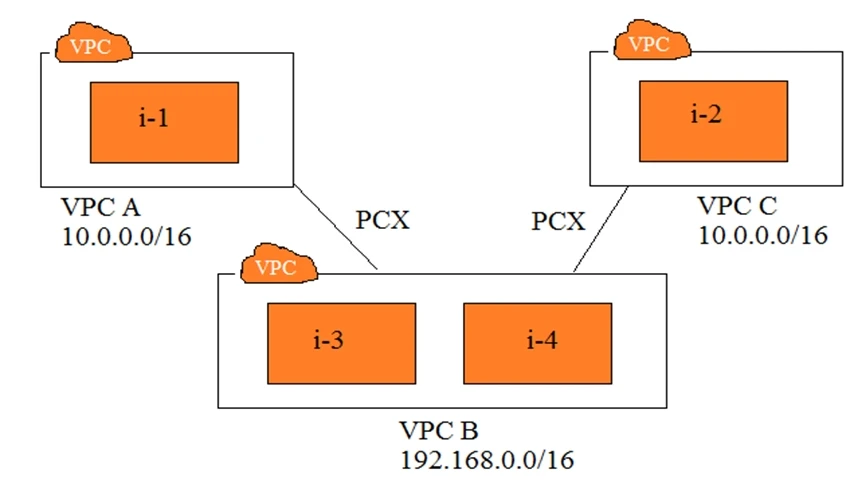
You have three VPCs: A, B, and C. VPCs A and C are both peered with VPC B. The IP address ranges are as follows:
✑ VPC A: 10.0.0.0/16
✑ VPC B: 192.168.0.0/16
✑ VPC C: 10.0.0.0/16
Instance i-1 in VPC A has the IP address 10.0.0.10. Instance i-2 in VPC C has the IP address 10.0.0.10. Instances i-3 and i-4 in VPC B have the IP addresses
192.168.1.10 and 192.168.1.20, respectively, i-3 and i-4 are in the subnet 192.168.1.0/24.
✑ i-3 must be able to communicate with i-1
✑ i-4 must be able to communicate with i-2
✑ i-3 and i-4 are able to communicate with i-1, but not with i-2.
Which two steps will fix this problem? (Choose two.)
The primary issue here is that i-4 cannot communicate with i-2 due to the overlapping IP ranges in VPC A and VPC C. The first necessary step is to change the IP address of i-2 in VPC C to eliminate the IP address conflict; for instance, changing it to 10.0.0.100. This ensures it has a unique address. Subsequently, you need to update the route tables in VPC B to direct traffic properly. Creating a new route table for VPC B with unique route entries for destinations VPC A and VPC C, utilizing more specific routes, will enable proper communication paths for the instances. Therefore, the most effective solutions are changing the IP address of i-2 and creating a new route table with specific routes.
Community votes
No votes yet
The best option for handling usage spikes up to millions of concurrent users while preserving the source IP addresses is to use a Network Load Balancer (NLB) with an Auto Scaling group of EC2 instances in a target group. The Network Load Balancer operates at the transport layer (Layer 4) and is capable of handling very high traffic volumes, making it suitable for applications with high concurrency. Additionally, the NLB preserves the source IP addresses of the clients, which is necessary for network traffic monitoring requirements.
Community votes
No votes yet