After you analyze your network environment, you decide to implement a full separation model for Internet access and MPLS L3VPN services.
For which reason do you make this decision?
After you analyze your network environment, you decide to implement a full separation model for Internet access and MPLS L3VPN services.
For which reason do you make this decision?
Implementing a full separation model for Internet access and MPLS L3VPN services enables EGP (Exterior Gateway Protocol) and IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) to operate independently. This separation is crucial because EGP is used to exchange routing information between different autonomous systems, while IGP is used within an autonomous system. By maintaining separate routing instances for each service, the network can achieve enhanced performance and stability, as it prevents routing conflicts and ensures each protocol operates within its optimal context.
Which statement about the Cisco MPLS TE forwarding adjacency feature is true?
The Cisco MPLS TE forwarding adjacency feature allows an MPLS Traffic Engineering tunnel to be advertised as a link in the Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) routing tables. This enables the MPLS core network to facilitate traffic engineering by providing the capability to include MPLS TE tunnels as part of the IGP’s topology.
While implementing TTL security, you issue the PE(config-router-af)#neighbor 2.2.2.2 ttl-security hops 2 command.
After you issue this command, which BGP packets does the PE accept?
When configuring TTL security with the command 'neighbor 2.2.2.2 ttl-security hops 2', the router expects to receive BGP packets from the neighbor with a TTL value of at least 253. This is calculated as 255 (the maximum TTL value) minus the number of hops set (2). Therefore, the correct answer is that the PE accepts packets from 2.2.2.2 with a TTL of 253 or more.

Refer to the exhibits. Which information is provided for traceback analysis when this configuration is applied?
The configuration provided refers to NetFlow, which is a protocol used for collecting IP traffic information. The command 'ip flow-export' designates where to send NetFlow data, and the 'ip flow ingress' command on the interface specifies that ingress traffic should be monitored. One crucial piece of information that NetFlow can provide for traceback analysis is the source interface of the traffic, which can help in determining the origin of the packets. This is especially useful in security monitoring and attack traceback scenarios.
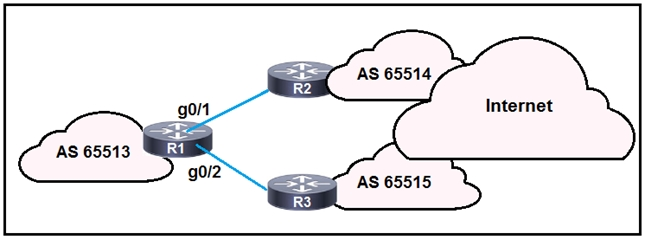
Refer to the exhibit. R1 is connected to two service providers and is under a DDoS attack.
Which statement about this design is true if URPF in strict mode is configured on both interfaces?
Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding (URPF) in strict mode helps prevent IP address spoofing by ensuring that packets received on an interface have a source IP address that matches the routing table's reverse path for that interface. In the strict mode, R1 will drop any traffic that enters an interface if the forwarding information base (FIB) entry for the source IP address does not match the interface the packet arrived on. This behavior is what option A describes. Therefore, this option is correct because it accurately reflects how URPF strict mode operates.