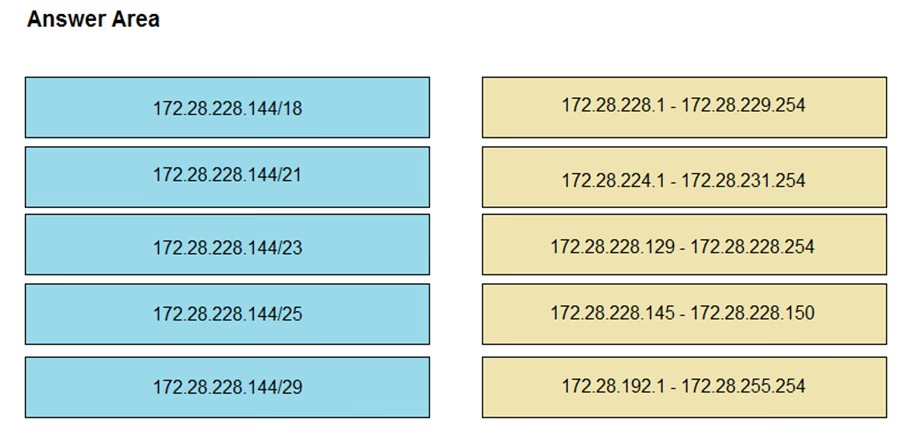
This subnet question requires us to grasp how to subnet very well. To quickly find out the subnet range, we have to find out the increment and the network address of each subnet. Let's take an example with the subnet 172.28.228.144/18:
From the /18 (= 1100 0000 in the 3rd octet), we find out the increment is 64. Therefore the network address of this subnet must be the greatest multiple of the increment but not greater than the value in the 3rd octet (228). We can find out the 3rd octet of the network address is 192 (because 192 = 64 * 3 and 192 < 228) -
> The network address is 172.28.192.0. So the first usable host should be 172.28.192.1 and it matches with the 5th answer on the right. In this case we don't need to calculate the broadcast address because we found the correct answer.
Let's take another example with subnet 172.28.228.144/23 -> The increment is 2 (as /23 = 1111 1110 in 3rd octet) -> The 3rd octet of the network address is 228
(because 228 is the multiply of 2 and equal to the 3rd octet) -> The network address is 172.28.228.0 -> The first usable host is 172.28.228.1. It is not necessary but if we want to find out the broadcast address of this subnet, we can find out the next network address, which is 172.28.(228 + the increment number).0 or
172.28.230.0 then reduce 1 bit -> 172.28.229.255 is the broadcast address of our subnet. Therefore the last usable host is 172.28.229.254.